Acne - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
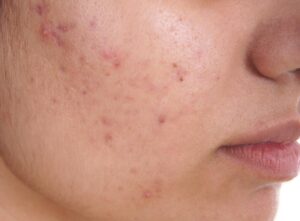
Acne is a common skin condition characterized by the inflammation of hair follicles and sebaceous (oil) glands. It primarily affects adolescents but can persist into adulthood. Acne manifests in various forms, including pimples, blackheads, whiteheads, and cysts. While conventional treatments are widely used, homeopathy offers a personalized approach aimed at treating the individual as a whole and addressing underlying imbalances.
Symptoms
Acne presents with a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity:
Mild Acne
- Comedones: Blackheads (open comedones) and whiteheads (closed comedones) are small, non-inflamed bumps on the skin.
- Papules: Small, red, raised bumps that may feel tender.
Moderate Acne
- Pustules: Inflamed, pus-filled bumps with a red base.
- Nodules: Large, painful, solid lumps beneath the skin’s surface.
Severe Acne
- Cysts: Deep, painful, pus-filled lumps that can cause scarring.
- Acne Conglobata: Severe form of acne with interconnected nodules and abscesses.
When to see a doctor
Seek medical advice if:
- Persistent Symptoms: Acne does not improve with over-the-counter treatments or worsens over time.
- Severe Pain: Acne causes significant pain or discomfort.
- Scarring: Acne leads to scarring or hyperpigmentation.
- Emotional Impact: Acne affects your self-esteem, causing emotional distress.
Causes
Acne results from a combination of factors that lead to the clogging of hair follicles and sebaceous glands:
- Hormonal Changes: Increased androgen levels during puberty stimulate sebaceous glands to produce more oil.
- Excess Oil Production: Overproduction of sebum contributes to the clogging of pores.
- Bacterial Infection: Propionibacterium acnes bacteria can proliferate in clogged pores, leading to inflammation.
- Dead Skin Cells: Accumulation of dead skin cells can block hair follicles.
- Inflammation: The body’s immune response to bacteria and clogged pores results in redness and swelling.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing acne:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Puberty, menstrual cycle, pregnancy, and hormonal disorders can exacerbate acne.
- Family History: A family history of acne may increase susceptibility.
- Diet: High-glycemic foods and dairy products may influence acne development.
- Stress: Increased stress levels can trigger or worsen acne.
- Cosmetic Use: Use of oily or comedogenic skincare products can contribute to acne.
Complications
Complications of acne can include:
- Scarring: Acne can lead to permanent scars or dark spots on the skin.
- Hyperpigmentation: Dark spots or patches can remain after acne lesions heal.
- Psychological Impact: Acne can contribute to anxiety, depression, and low self-esteem.
Preventions
To reduce the risk of acne or prevent its worsening:
- Maintain Good Skin Hygiene: Cleanse the skin regularly to remove excess oil and dirt.
- Avoid Picking or Squeezing: Resist the urge to pick or squeeze acne lesions to prevent scarring and infection.
- Use Non-Comedogenic Products: Choose skincare and cosmetic products that do not clog pores.
- Manage Stress: Implement stress-reducing techniques such as exercise, meditation, or counseling.
- Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while limiting sugary and greasy foods.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to acne management, focusing on treating the individual’s overall health and constitution. Homeopathic remedies are selected based on specific symptoms and individual characteristics. Commonly used remedies include:
- Sulphur: For acne with intense itching, burning sensations, and inflammation, especially if the skin is greasy and prone to infections.
- Hepar Sulphuris: Useful for painful, pus-filled acne that is sensitive to touch and may feel better with warmth.
- Natrum Muriaticum: For acne that is aggravated by emotional stress or occurs in individuals with a dry, sensitive skin type.
- Pulsatilla: For acne that worsens around the menstrual period or in individuals who experience mood swings and have a tendency to cry easily.
- Arsenicum Album: For acne with a tendency to dry out, with symptoms of restlessness and anxiety.
A homeopathic practitioner will tailor the remedy to suit the patient’s overall condition and specific symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing acne typically involves:
- Clinical Examination: A visual inspection of the skin to assess the type, severity, and distribution of acne lesions.
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s medical history, including any recent changes in lifestyle, diet, or stress levels.
- Skin Tests: In some cases, skin tests may be conducted to rule out other conditions or assess bacterial involvement.
Treatment
Treatment options for acne can include:
- Topical Treatments: Over-the-counter and prescription creams or gels containing ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, or retinoids.
- Oral Medications: Antibiotics or hormonal therapies prescribed by a healthcare provider.
- Professional Procedures: Treatments such as chemical peels, laser therapy, or light therapy to reduce acne and improve skin appearance.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Adjustments in diet, stress management, and skincare routines.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Several lifestyle and home remedies can support acne management:
- Gentle Cleansing: Use a mild, non-comedogenic cleanser to wash your face twice daily.
- Exfoliation: Regularly exfoliate to remove dead skin cells and prevent clogged pores.
- Tea Tree Oil: Apply diluted tea tree oil for its antimicrobial properties.
- Green Tea: Use green tea extracts or apply cooled green tea bags to the skin to reduce inflammation.
- Aloe Vera: Apply aloe vera gel to soothe irritated skin and reduce redness.
Preparing for your appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of your acne symptoms, including their frequency, location, and any triggers.
- Medical History: Provide information about any previous treatments or medications used.
- Lifestyle Factors: Share details about your diet, stress levels, and skincare routine.
- Goals and Concerns: Be clear about your goals for treatment and any specific concerns you have about managing acne.
- Questions: Prepare a list of questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and management strategies.
