Alzheimer's Disease - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
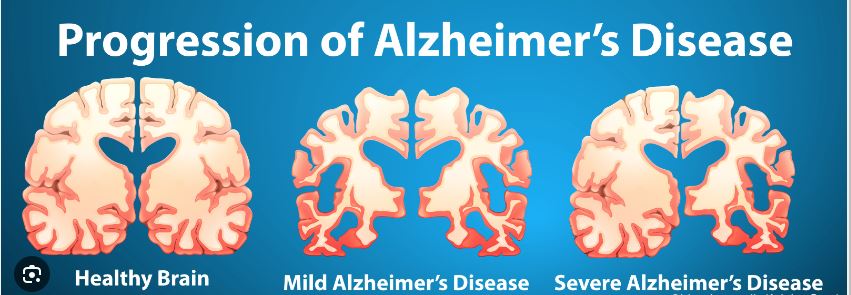
Alzheimer’s disease is a progressive neurological disorder that leads to the deterioration of cognitive functions, including memory, thinking, and reasoning. It is the most common cause of dementia, affecting millions of people worldwide. The condition worsens over time, eventually impairing the ability to perform everyday tasks. While there is no cure for Alzheimer’s, early diagnosis and a combination of medical and holistic approaches can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Symptoms
Alzheimer’s disease presents with a range of symptoms, which typically develop slowly and worsen over time:
- Memory Loss: Difficulty remembering recent events, conversations, or appointments.
- Confusion: Disorientation about time, place, or identity of people.
- Difficulty with Language: Problems finding the right words or following conversations.
- Disorganized Thinking: Trouble planning, organizing, or solving problems.
- Poor Judgment: Making poor decisions or showing a lack of insight.
- Behavioral Changes: Mood swings, personality changes, or withdrawal from social activities.
- Loss of Motor Skills: Difficulty with coordination, balance, or performing familiar tasks.
- Visual and Spatial Difficulties: Trouble understanding visual images and spatial relationships.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you or a loved one experience:
- Memory Problems: Significant and persistent memory loss affecting daily life.
- Confusion: Increasing confusion or disorientation about time and place.
- Behavioral Changes: Noticeable changes in personality or behavior that interfere with daily functioning.
- Difficulty with Daily Tasks: Challenges in performing familiar activities or responsibilities.
- Family History: A family history of Alzheimer’s or other forms of dementia.
Early diagnosis allows for timely intervention and management, which can help slow the progression of the disease.
Causes
The exact cause of Alzheimer’s disease remains unknown, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors: Certain genes are associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer’s, including the APOE ε4 gene.
- Protein Abnormalities: Accumulation of amyloid plaques and tau tangles in the brain disrupts normal brain function.
- Neurodegeneration: Progressive loss of neurons and synapses in the brain.
- Inflammation: Chronic inflammation in the brain may contribute to disease progression.
- Vascular Factors: Impaired blood flow and vascular damage in the brain.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease:
- Age: The risk increases with age, especially after 65.
- Family History: A family history of Alzheimer’s or other dementias.
- Genetics: Inherited genetic mutations or the presence of certain genes.
- Down Syndrome: Individuals with Down syndrome are at a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
- Cardiovascular Health: Conditions such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Head Injuries: History of traumatic brain injuries or concussions.
- Lifestyle Factors: Sedentary lifestyle, poor diet, and smoking.
Complications
Alzheimer’s disease can lead to several complications:
- Infections: Increased susceptibility to infections, such as pneumonia, due to impaired physical function.
- Falls: Higher risk of falls and fractures due to balance and coordination issues.
- Malnutrition: Difficulty in eating or swallowing can lead to weight loss and malnutrition.
- Behavioral Problems: Aggression, agitation, or severe mood swings can impact social interactions and caregiving.
- Dependency: Increased dependency on caregivers for daily activities and personal care.
Preventions
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent Alzheimer’s disease, certain strategies may reduce the risk:
- Healthy Diet: Follow a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to support cardiovascular and brain health.
- Mental Stimulation: Participate in activities that challenge the brain, such as puzzles, reading, and learning new skills.
- Social Engagement: Maintain social connections and participate in community activities.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Control risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and high cholesterol.
- Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol: Refrain from smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing Alzheimer’s disease by addressing individual symptoms and overall well-being. Remedies are selected based on the patient’s unique presentation and constitutional type. Common homeopathic remedies for Alzheimer’s may include:
Homeopathic Remedies for Alzheimer’s Disease
A homeopathic practitioner will select the appropriate remedy based on a detailed assessment of the patient’s symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Alzheimer’s disease involves several steps:
- Medical History: A thorough review of symptoms, medical history, and family history of dementia.
- Neurological Examination: Assessment of cognitive function, memory, and neurological health.
- Cognitive Testing: Standardized tests to evaluate memory, thinking, and problem-solving skills.
- Brain Imaging: MRI or CT scans to rule out other conditions and assess brain changes.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to identify possible underlying conditions or nutrient deficiencies.
Treatments
Treatment for Alzheimer’s disease typically includes a combination of medical, supportive, and lifestyle interventions:
Conventional Treatments
Medications:
- Cholinesterase Inhibitors: Such as donepezil, rivastigmine, and galantamine, which help improve cognitive function.
- NMDA Receptor Antagonists: Such as memantine, which may help with moderate to severe symptoms.
Supportive Therapies:
- Cognitive Therapy: Strategies to help manage cognitive decline and improve quality of life.
- Occupational Therapy: Assistance with daily activities and adapting the living environment.
Caregiver Support:
- Counseling and Education: Providing support and training for caregivers to manage the challenges of caregiving.
Homeopathic Treatments
Homeopathic remedies can complement conventional treatments and support overall well-being:
- Arsenicum Album: For anxiety, restlessness, and memory issues, especially with a tendency towards compulsive behaviors.
- Calcarea Phosphorica: For cognitive decline with fatigue and weakness, often seen in younger patients.
- Natrum Sulphuricum: For memory loss and mental fatigue associated with a history of trauma or emotional stress.
- Anacardium Orientale: For memory problems and cognitive decline with feelings of inadequacy or self-doubt.
- Cimicifuga: For mood swings and memory issues, especially if associated with physical and emotional stress.
Impact on Life
Alzheimer’s disease can have a profound impact on a person’s life and the lives of their family and caregivers. As the disease progresses, the following challenges may arise:
Dependence on Others: Individuals with Alzheimer’s may become increasingly dependent on others for assistance with daily activities, such as dressing, eating, and bathing.
Safety Concerns: The decline in memory and cognitive abilities can lead to safety risks, such as forgetting to turn off appliances or wandering and getting lost.
Communication Difficulties: As the disease affects language skills, individuals may have difficulty expressing themselves or understanding others, leading to frustration and isolation.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: Alzheimer’s can cause confusion, fear, and feelings of helplessness, leading to emotional distress for both the affected person and their loved ones.
Caregiver Burden: Family members and caregivers may experience significant emotional, physical, and financial strain while providing care and support to someone with Alzheimer’s.
Financial Challenges: Managing finances can become challenging as the disease progresses, putting the affected person at risk of financial exploitation.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage Alzheimer’s disease and improve quality of life:
- Maintain a Routine: Establish a daily routine to provide structure and reduce confusion.
- Engage in Cognitive Activities: Encourage activities that stimulate the brain, such as puzzles, games, and learning new skills.
- Promote Physical Activity: Encourage regular exercise to support overall health and well-being.
- Ensure Safety: Modify the living environment to ensure safety and reduce the risk of accidents.
- Provide Social Interaction: Foster social connections and engage in meaningful activities to support emotional health.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment, consider the following:
- Symptom Record: Keep a detailed record of symptoms, including their onset, duration, and progression.
- Medical History: Provide comprehensive information about previous medical conditions, family history, and current medications.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and management strategies.
- Support System: Involve family members or caregivers in the appointment to discuss care strategies and support.
