Parkinson's disease - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
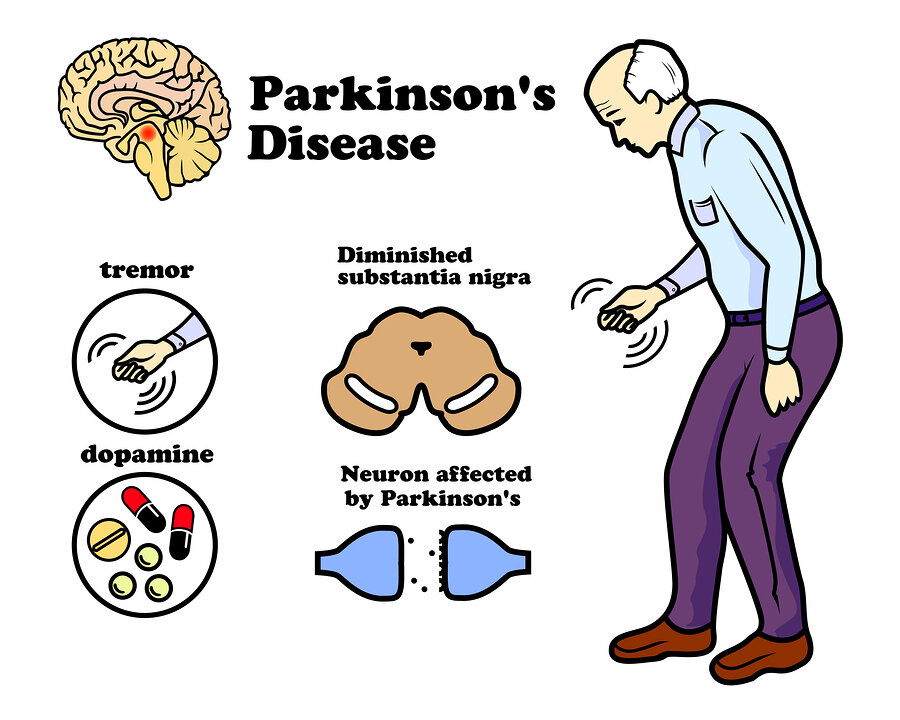
Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain. This results in motor and non-motor symptoms that affect daily life and overall well-being. While conventional treatments focus on managing symptoms and slowing progression, homeopathy offers a holistic approach to support and complement these treatments.
Symptoms
Parkinson’s Disease manifests with a range of symptoms that can be categorized into motor and non-motor symptoms.
Motor Symptoms
- Tremors: Involuntary shaking, usually starting in one hand or limb.
- Bradykinesia: Slowness of movement, making daily tasks more challenging.
- Rigidity: Muscle stiffness, leading to reduced range of motion and discomfort.
- Postural Instability: Difficulty maintaining balance, increasing the risk of falls.
- Resting Tremor: Tremors that occur when the muscles are at rest, typically in one hand.
- Shuffling Walk: Small, shuffling steps with reduced arm swing.
Non-Motor Symptoms
- Cognitive Changes: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and slowed thinking.
- Sleep Disorders: Difficulty falling or staying asleep, and restless legs.
- Mood Disorders: Depression, anxiety, or emotional flatness.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Issues such as constipation, urinary problems, and reduced sweating.
- Speech Changes: Soft or slurred speech, and difficulty with articulation.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Motor Symptoms: Noticeable tremors, slowness of movement, or difficulty with coordination.
- Non-Motor Symptoms: Significant changes in cognition, mood, or sleep patterns.
- Progressive Symptoms: Symptoms that worsen over time or significantly impact daily life.
- Difficulty with Daily Activities: Challenges in performing routine tasks or maintaining independence.
Causes
The exact cause of Parkinson’s Disease remains unclear, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Genetic Factors: Genetic mutations and family history may increase susceptibility.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to certain toxins or chemicals might contribute to the risk.
- Age: The risk of developing Parkinson’s increases with age.
- Neurodegeneration: Progressive loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, particularly in the substantia nigra.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing Parkinson’s Disease:
- Age: Most commonly affects individuals over the age of 60.
- Family History: A family history of Parkinson’s Disease or other neurodegenerative disorders.
- Gender: Men are slightly more likely to develop Parkinson’s than women.
- Exposure to Toxins: Long-term exposure to pesticides, herbicides, or other chemicals.
- Head Trauma: History of significant head injuries or traumatic brain injury.
Complications
Parkinson’s Disease can lead to a variety of complications:
- Motor Complications: Worsening of motor symptoms, including freezing of gait and dyskinesias.
- Cognitive Decline: Progression to Parkinson’s dementia or significant cognitive impairment.
- Depression and Anxiety: Emotional challenges that affect quality of life.
- Falls and Injuries: Increased risk of falls and related injuries due to balance issues.
- Swallowing Problems: Difficulty swallowing, which can lead to choking or aspiration pneumonia.
Preventions
While Parkinson’s Disease cannot be completely prevented, certain measures may reduce the risk or delay onset:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in physical activity to maintain mobility and balance.
- Healthy Diet: Consuming a balanced diet rich in antioxidants and nutrients.
- Avoiding Toxins: Minimizing exposure to environmental toxins and pollutants.
- Protecting the Head: Wearing helmets during activities with a risk of head injury.
- Genetic Counseling: For those with a family history, seeking genetic counseling may provide insights into risk.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy can offer a supportive approach to managing Parkinson’s Disease by addressing individual symptoms and overall well-being. Remedies are selected based on a thorough evaluation of the patient’s physical, emotional, and mental state. Potential remedies include:
- Belladonna: For acute tremors and sudden changes in symptoms.
- Gelsemium: For muscle weakness and trembling, especially with fatigue.
- Nux Vomica: For digestive issues and rigidity, particularly in stressed individuals.
- Stramonium: For severe agitation and mental disturbances.
- Lycopodium: For cognitive decline and low self-confidence, often accompanied by digestive issues.
A homeopathic practitioner will tailor remedies to the specific needs of each patient.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Parkinson’s Disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation and diagnostic tests:
- Clinical Assessment: Detailed medical history, physical examination, and neurological assessment.
- Imaging: MRI or CT scans to rule out other conditions and assess brain structure.
- DaTscan: A specialized imaging technique to evaluate dopamine transporter levels in the brain.
- Blood Tests: To exclude other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatments
Treatment for Parkinson’s Disease aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life:
- Medications: Including levodopa, dopamine agonists, and MAO-B inhibitors to manage motor symptoms.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and therapies to improve mobility, balance, and strength.
- Occupational Therapy: Assistance with daily activities and adaptive strategies.
- Speech Therapy: To address speech and swallowing difficulties.
- Homeopathy: Complementary approach to manage symptoms and support overall well-being.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can support overall health and complement treatment plans:
- Regular Exercise: Engaging in activities such as walking, swimming, or tai chi to improve mobility and balance.
- Balanced Diet: Consuming a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated to support overall health and digestive function.
- Sleep Hygiene: Maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and creating a restful environment.
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or yoga to reduce stress.
- Support Groups: Connecting with support groups or community resources for social support and shared experiences.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of symptoms, including their frequency and impact on daily life.
- Medical History: Provide a comprehensive history of medical conditions, medications, and treatments.
- Family History: Share any relevant family history of neurological or movement disorders.
- Questions and Concerns: Prepare a list of questions about diagnosis, treatment options, and management strategies.
- Support System: Consider bringing a family member or caregiver to discuss the individual’s needs and support.
- Daily Impact: Describe how Parkinson’s Disease affects daily life, including work, relationships, and self-care.
Parkinson’s disease is a condition that affects the brain and causes problems with movement. Here’s a simple explanation:
Parkinson’s Disease: Parkinson’s disease is a brain disorder that happens when certain cells in the brain don’t work properly. These cells produce a chemical called dopamine, which helps control movement. When these cells die or become damaged, the brain can’t send the right signals to the muscles, making it harder for a person to move smoothly.
Symptoms of Parkinson’s Disease: People with Parkinson’s disease may experience:
Tremors: Shaking or trembling in the hands, arms, legs, or jaw, especially when at rest.
Slowness of Movement: Movements become slower, making everyday tasks take longer.
Muscle Stiffness: The muscles may feel tight and rigid, causing discomfort.
Balance Problems: Difficulty maintaining balance, leading to a higher risk of falls.
Trouble with Coordination: It becomes harder to perform precise movements.
Screening Tests: There are no specific tests to diagnose Parkinson’s disease definitively, but doctors may use certain assessments to evaluate a person’s symptoms and rule out other conditions. The diagnosis is mainly based on a person’s medical history and physical examination.
Impact on Life and Quality of Life: Parkinson’s disease can significantly affect a person’s life and well-being. As the disease progresses, it may lead to:
Difficulty with Daily Activities: Simple tasks like dressing, eating, and writing can become challenging.
Loss of Independence: As the ability to move and take care of oneself declines, individuals may become more dependent on others for help.
Emotional and Psychological Impact: Coping with the physical limitations and the uncertainty of the disease can cause emotional distress and anxiety.
Social Isolation: Due to movement difficulties and self-consciousness about symptoms, people with Parkinson’s may withdraw from social activities.
Increased Falls and Injuries: Balance problems and coordination issues can lead to a higher risk of falls and potential injuries.
Communication Challenges: Speech may become softer and harder to understand, impacting communication with others.
Despite these challenges, early diagnosis and appropriate management can help improve the quality of life for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Medications, physical therapy, and support from healthcare professionals can make a significant difference in managing symptoms and maintaining functionality as much as possible. Support from family and friends is also crucial in helping individuals with Parkinson’s disease navigate their daily lives and maintain social connections.
