Molluscum Contagiosum -
Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
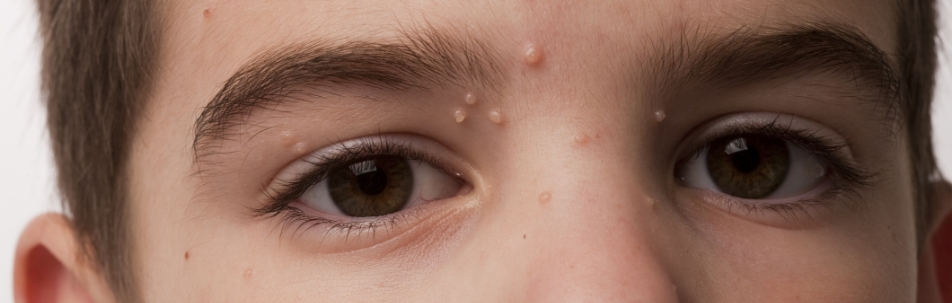
Molluscum contagiosum is a viral skin infection caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). It results in benign, raised, flesh-colored lesions or bumps on the skin. These lesions can appear anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, arms, and hands in children, and on the genital area, lower abdomen, and inner thighs in adults. The infection is generally self-limiting, meaning it can resolve on its own without treatment over several months to years. However, homeopathic remedies can help expedite the healing process and alleviate symptoms.
Symptoms
The primary symptom of molluscum contagiosum is the appearance of small, firm, and dome-shaped bumps on the skin. These bumps typically:
- Are flesh-colored and have a dimple or indentation in the center.
- Measure about 2 to 5 millimeters in diameter.
- May become red and inflamed as the body fights off the virus.
- Can be itchy or uncomfortable, but are generally not painful.
- Appear singly or in groups and can spread through scratching or rubbing.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a healthcare provider if:
- The lesions are widespread or persistent, lasting more than a few months without signs of improvement.
- The bumps become red, swollen, or painful, indicating a possible secondary bacterial infection.
- You have a weakened immune system due to conditions such as HIV/AIDS or immunosuppressive medications, as this can lead to more severe and prolonged infections.
- Lesions appear on sensitive areas such as the eyelids or genital area, causing discomfort or complications.
Causes
Molluscum contagiosum is caused by a poxvirus known as the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV). The virus spreads through:
- Direct skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
- Touching contaminated objects such as towels, clothing, toys, or gym equipment.
- Sexual contact, making it a sexually transmitted infection (STI) in adults.
- Self-inoculation, where the virus spreads from one part of the body to another through scratching or rubbing.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of contracting molluscum contagiosum:
- Age: Children between the ages of 1 and 10 are more commonly affected.
- Close Contact: Living in close quarters, such as in households or schools, can facilitate the spread of the virus.
- Sexual Activity: Adults who are sexually active are at higher risk, particularly those with multiple partners.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible to severe infections.
- Skin Conditions: Eczema or other conditions that damage the skin barrier can increase the risk of infection.
Complications
While molluscum contagiosum is usually benign and self-limiting, complications can arise, including:
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial infections can develop if the lesions are scratched or become inflamed.
- Scarring: Lesions may leave scars, especially if they become infected or are forcibly removed.
- Spread of Lesions: Scratching or rubbing the bumps can lead to the spread of lesions to other parts of the body.
- Emotional Distress: Visible lesions, particularly on the face or genital area, can cause emotional distress or self-esteem issues.
Preventions
Preventing molluscum contagiosum involves minimizing exposure to the virus and maintaining good hygiene practices:
- Avoid Skin-to-Skin Contact: Refrain from direct contact with infected individuals or lesions.
- Do Not Share Personal Items: Avoid sharing towels, clothing, or other personal items with others.
- Practice Safe Sex: Use condoms and practice safe sex to reduce the risk of sexually transmitted infections.
- Keep Lesions Covered: Cover lesions with clothing or bandages to prevent the spread of the virus.
- Good Hygiene: Wash hands frequently and avoid touching or scratching lesions.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to treating molluscum contagiosum by addressing the underlying immune response and promoting natural healing. Common homeopathic remedies include:
- Thuja Occidentalis: Often used for warts and skin lesions, including molluscum contagiosum. It helps boost the immune system and reduce lesions.
- Calcarea Carbonica: Suitable for individuals with multiple lesions, particularly if they are prone to catching infections easily.
- Antimonium Crudum: Useful for crusty, warty lesions that are painful and itchy.
- Sulphur: Effective for itchy and inflamed lesions, especially if they worsen with heat or bathing.
- Natrum Muriaticum: Helps in cases where lesions are accompanied by dry skin and a tendency to develop cold sores.
A qualified homeopathic practitioner will conduct a comprehensive assessment to select the most appropriate remedy based on the individual’s overall health and specific symptoms.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing molluscum contagiosum typically involves:
- Clinical Examination: Visual inspection of the characteristic lesions by a healthcare provider.
- Biopsy: In rare cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other skin conditions.
- Medical History: A review of the patient’s medical history, including any recent skin infections or contact with infected individuals.
Treatment
While molluscum contagiosum often resolves on its own, various treatment options can help speed up recovery and reduce symptoms:
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the lesions with liquid nitrogen to remove them.
- Curettage: Scraping off the lesions with a sharp instrument.
- Topical Treatments: Applying creams or ointments containing salicylic acid, retinoids, or antiviral agents.
- Laser Therapy: Using laser treatments to remove stubborn lesions.
- Homeopathic Remedies: Individualized homeopathic treatments to stimulate the body’s natural healing processes and enhance the immune response.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can support skin health and manage molluscum contagiosum:
- Keep Lesions Clean: Wash the affected area gently with mild soap and water.
- Avoid Scratching: Refrain from scratching or picking at the lesions to prevent spreading and secondary infections.
- Use Moisturizers: Apply fragrance-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated and reduce irritation.
- Natural Remedies: Some natural remedies, such as tea tree oil or apple cider vinegar, may help reduce lesions, but consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Healthy Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can support the immune system and overall skin health.
Preparing for your appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of the lesions’ development, including any changes in size, color, and symptoms.
- Medical History: Provide information about any previous skin conditions, treatments, and contact with infected individuals.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes to manage molluscum contagiosum.
- Current Medications: List any current medications or supplements you are taking, including any topical treatments.