Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
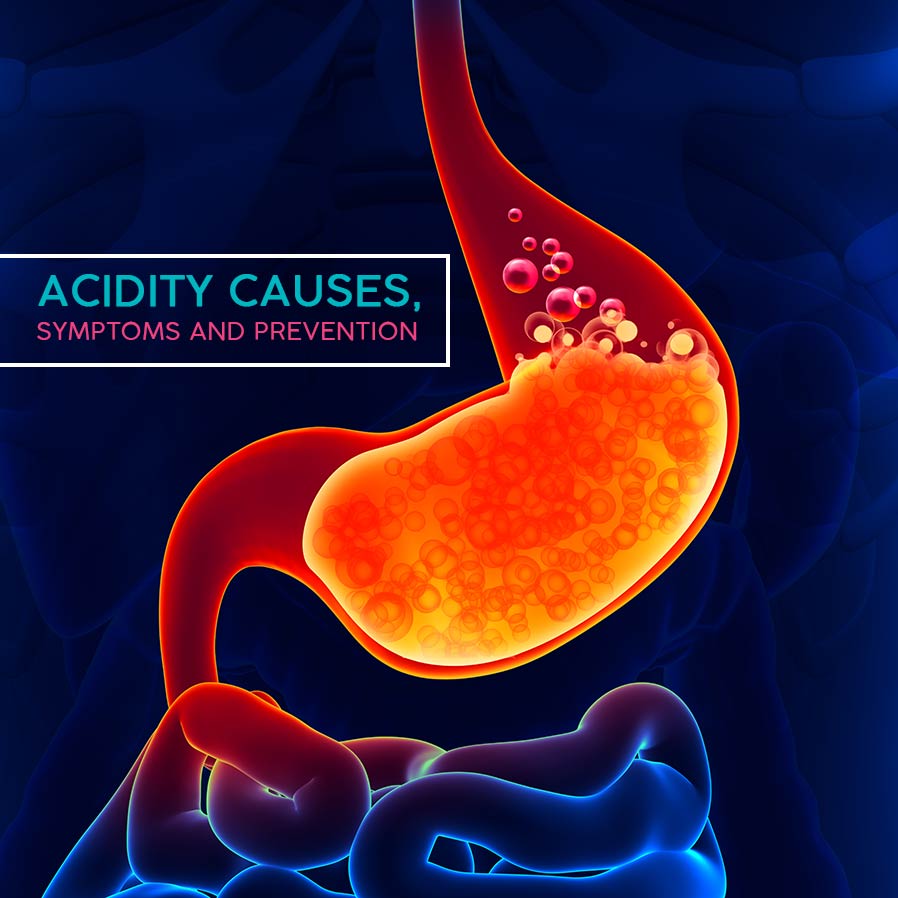
Gastro Esophageal Reflux Disease
Gastro-esophageal reflux disease or acid reflux disease or GERD is a condition in which the contents of the stomach reflux back into the esophagus (food pipe). Since the stomach contents are acidic in nature, this damages the inner lining of the food pipe and causes symptoms of heartburn, pain, etc.
GERD is observed in adults as well as kids. The kids may have somewhat different symptomatology.
GERD is treatable by homeopathy effectively, without adverse effects or without using habit-forming drugs.
Homeopathic medicine for Acid Reflux:
Homeopathy aims at treating the root cause of GERD.
Homeopathic medicines have the capacity to restore the abnormal functioning of the oesophageal sphincter.
The medicines also help in balancing the metabolism and correcting digestive errors.
A combination of well taken homeopathic case history with diet and lifestyle changes helps in offering a sustainable recovery to the patients.
How homeopathy can help in GERD?
Homeopathy treats the disease at the root and tries to correct the functioning of the digestive system. In turn, it regulates acid secretion and digestion.
- Initially, homeopathic medicines provide you relief from symptoms, such as heartburn, acidity, chest pain, sour taste, etc.
- In mild to moderate cases of GERD, it may help to strengthen the muscles of the lower esophageal sphincter and prevent the backflow of stomach content.
- If you are taking antacids for a long, period homeopathy may help to reduce the dependency on antacids or other conventional medicines.
- Homeopathic treatment for GERD is completely safe and non-habit-forming. Results in homeopathy for GERD are long-lasting.
What are the chances of recovery from GERD with homeopathy?
Excellent result: Excellent results can be observed in mild, moderate, and early-detected & treated cases of GERD
Good results: Good results can be observed by using homeopathy in moderate to severe cases. Also, in 3-7 years old cases, one may find good results by using homeopathy.
Scope and duration of homeopathic treatment
Homeopathy can be opted as the first line of treatment in early detected cases with mild to moderate symptoms. This helps in early resolution of the disease with fewer chances of relapse. Homeopathy can also opt as a supportive form of treatment for patients with chronic GERD who are on long-term conventional treatment.
The duration of the treatment varies from one patient to another. Associated diseases usually prolong the duration of treatment. But the time taken for recovery is definitely less in mild to moderate cases compared to severe ones.
Duration of treatment:
As per our experience in treating patients of GERD most of the patients respond to the treatment in the initial six to eight weeks, but the total duration of treatment may vary depending on various factors listed here.
- The extent of the disease
- Cause behind GERD
- Duration of the suffering
- Other underlying medical conditions
- Current and past medication
- Lifestyle and dietary habits of the patient
Causes of GERD
There are multiple causes responsible for initiating GERD, and different causes may be functioning in different individuals or even in the same individual at different times. The commonest causes responsible for GERD have been listed below:
1)Delayed emptying of the stomach:
When food remains in the stomach for a longer duration, the stomach is distended for a longer time and this increases the chances of reflux of the stomach contents.
There are several other contributing factors for GERD which are as follow
2)Faulty diet:
- Eating an excess of spicy food, pungent food, or fatty food
- Having an excess of coffee or aerated drinks
- Eating citrus fruits
- Excess use of garlic or onion in the diet
- Using chocolates or peppermints
3) Faulty eating habits
- Eating large meals at a time
- Eating late at night
- A long gap between two meals
- Lying down immediately after eating
- A poor posture after eating
- 4)Faulty lifestyle
- Excess smoking
- Excess use of alcohol
- Lack of sleep
- Lack of exercise
- 5)Drugs: Calcium channel blockers, antihistamines, theophylline, nitrates,
6) Stress: Though this has not been directly linked to GERD, most patients report an increase in their symptoms during stressful times.
7) Other contributory conditions: Obesity, pregnancy, diabetes, obesity, rapid weight gain, etc.
8)Functional abnormalities of the lower esophageal sphincter
-> Abnormally weak contractions of the sphincter
-> Abnormal relaxations of the sphincter
Both of the above contribute to increased chances of backflow of the stomach contents into the esophagus.
9)Hiatus Hernia:
A condition in which there is the protrusion of the stomach up into the opening normally occupied by the esophagus in the diaphragm [the muscle that separates the chest (thoracic) cavity from the abdomen.
10)Abnormal esophageal contractions:
Co-ordinated esophageal contractions cause the forward movement of food from the esophagus into the stomach. When the wave of contraction is defective, the refluxed acid is not pushed back into the stomach and it can cause damage to the lining of the esophagus.
Symptoms of GERD
Uncomplicated GERD presents with the following symptoms commonly:
- Heartburn: This is the commonest presentation of GERD. Patients often complain of burning pain in the middle of the chest region (retrosternal). The pain may also be present in the upper part of the abdomen and sometimes travels up to the throat. Occasionally the pain may be sharp or pressing instead of burning. The pain is worse after meals and can last up to a couple of hours. Symptoms may be worse on lying down.
- Regurgitation: The refluxed stomach contents may come into the throat or mouth and this may occur especially on bending or sleeping. There may be a feeling of ‘something stuck in the throat’.
- Respiratory symptoms: A dry cough, hoarseness of voice, bad taste in the mouth are other symptoms caused due to the regurgitation of the food.
- Occasionally patients may develop nausea (though this is not very frequent) and GERD should always be considered in patients who have unexplained nausea.
- GERD in children: In children, the common symptoms are vomiting, coughing, and other respiratory problems.
Lifestyle Changes for GERD Patients
Patients with GERD can benefit immensely if they follow the following set of instructions and incorporate these into their daily lives. These changes in lifestyle can significantly alleviate most of the symptoms of GERD.
- Don’t eat at least 2-3 hours before bedtime. This will help to empty the stomach before the person goes into the reclined position and will prevent reflux.
- Don’t lie down right after eating at any time of day.
- Keep the head end of your bed elevated by at least 6 inches with blocks because gravity helps in preventing the reflux of the acid from the stomach.
- Don’t eat large meals; instead opt for smaller, more frequent meals throughout the day.
- Give up smoking because smoking weakens the lower esophageal sphincter and increases reflux.
- Avoid alcohol because it increases the likelihood that acid from your stomach will back up.
- Reduce your weight if you are overweight because obesity increases the chances of reflux of the acid.
- Avoid fatty, greasy foods, chocolate, caffeine, spicy foods, citrus foods, and other things which worsen your heartburn.
- Avoid remaining in stooped posture; keep an upright posture when standing or sitting.
- Be cautious with over-the-counter painkillers as these might worsen your complaints.
Stay Healthy and Take Care !!
Overview
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) is a chronic digestive condition where stomach acid or bile flows back into the esophagus, leading to irritation and discomfort. This reflux occurs due to the malfunctioning of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which normally prevents stomach contents from flowing back up. GERD is a common condition that can significantly impact quality of life, but understanding its symptoms, causes, and treatment options—including homeopathic remedies—can provide relief and management strategies.
Symptoms
GERD can present with a variety of symptoms, including:
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest, often after eating or lying down.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of acid or bile rising up from the stomach into the throat or mouth.
- Chest Pain: Discomfort or pain in the chest, which can sometimes be mistaken for heart-related issues.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing or a feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Chronic Cough: Persistent cough that is not related to respiratory infections.
- Hoarseness: Changes in voice or hoarseness due to irritation of the vocal cords by stomach acid.
- Sore Throat: Persistent sore throat or irritation, especially in the morning.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Frequent Symptoms: Persistent or severe heartburn and acid reflux that occurs more than twice a week.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Trouble swallowing or a feeling of a lump in the throat.
- Unexplained Weight Loss: Significant weight loss without a clear cause.
- Severe Chest Pain: Chest pain that is severe or worsens over time, especially if it radiates to the arms or jaw.
- Persistent Cough: A chronic cough or hoarseness that does not improve with over-the-counter remedies.
Causes
GERD is primarily caused by the malfunction of the lower esophageal sphincter (LES), which can result from:
- LES Dysfunction: A weakened or relaxed LES allows stomach acid to flow back into the esophagus.
- Hiatal Hernia: A condition where part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, affecting LES function.
- Increased Abdominal Pressure: Conditions or activities that increase pressure in the abdomen, such as obesity or pregnancy.
- Delayed Gastric Emptying: Slower emptying of the stomach can lead to increased acid production and reflux.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing GERD:
- Obesity: Excess body weight can increase pressure on the abdomen, contributing to acid reflux.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased abdominal pressure during pregnancy can exacerbate GERD symptoms.
- Smoking: Tobacco use can weaken the LES and contribute to acid reflux.
- Diet: Consumption of certain foods and beverages, such as fatty foods, caffeine, alcohol, and chocolate, can trigger GERD symptoms.
- Medications: Some medications, such as certain antihistamines, calcium channel blockers, and sedatives, can relax the LES and contribute to GERD.
Complications
If left untreated, GERD can lead to several complications:
- Esophagitis: Inflammation and irritation of the esophagus due to repeated exposure to stomach acid.
- Esophageal Ulcers: Sores or ulcers in the lining of the esophagus caused by chronic acid exposure.
- Strictures: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue formation from chronic inflammation.
- Barrett’s Esophagus: A condition where the lining of the esophagus changes, which can increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
- Respiratory Issues: Chronic cough, asthma, or laryngitis resulting from acid reflux affecting the respiratory tract.
Preventions
While it may not be possible to completely prevent GERD, the following strategies can help manage and reduce symptoms:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce abdominal pressure and GERD symptoms.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Identify and avoid foods and beverages that trigger GERD symptoms, such as spicy foods, caffeine, and alcohol.
- Eat Smaller Meals: Consume smaller, more frequent meals instead of large meals to minimize acid production.
- Avoid Lying Down After Eating: Wait at least three hours after eating before lying down or going to bed to prevent acid reflux.
- Elevate the Head of the Bed: Sleeping with the head of the bed elevated can help reduce nighttime reflux.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing GERD by addressing individual symptoms and underlying imbalances. Commonly used homeopathic remedies include:
- Nux Vomica: For symptoms related to indigestion, heartburn, and irritability due to overeating or stress.
- Lycopodium: For bloating, digestive discomfort, and acid reflux with a sensation of fullness.
- Carbo Veg: For symptoms of bloating, gas, and acid reflux with a feeling of heaviness in the stomach.
A homeopathic practitioner can provide personalized remedies and treatment plans based on individual symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing GERD involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms, dietary habits, and overall health.
- Physical Examination: A physical exam to assess symptoms and any potential complications.
- Endoscopy: An endoscopic procedure to visualize the esophagus and assess for inflammation, ulcers, or other abnormalities.
- Esophageal pH Monitoring: A test to measure the amount of acid in the esophagus over a 24-hour period.
- Manometry: A test to measure the pressure and function of the LES and esophageal muscles.
Treatments
Treatment for GERD may include:
- Medications: Over-the-counter or prescription medications such as antacids, H2 receptor antagonists, or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) to reduce acid production and manage symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Modifications in diet, weight management, and eating habits to reduce symptoms.
- Surgical Options: In severe cases, surgical procedures such as fundoplication may be considered to strengthen the LES and reduce acid reflux.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home remedies can support symptom management:
- Healthy Eating: Incorporate a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid foods that trigger GERD symptoms.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in moderate physical activity to support overall health and manage weight.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to aid digestion and help manage symptoms.
- Herbal Remedies: Herbal teas such as chamomile or ginger may help soothe the digestive tract and reduce symptoms.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner, consider:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of symptoms, including their onset, frequency, and impact on daily life.
- List Medications and Supplements: Bring information about any current medications or supplements you are taking.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns you have about your symptoms, treatment options, and overall health.
- Health History: Provide a comprehensive overview of your health history, including any existing conditions, dietary habits, and previous treatments.
