Pityriasis - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
Pityriasis refers to a group of common skin conditions that cause scaling and rashes. The term encompasses various disorders, including pityriasis rosea, pityriasis alba, and pityriasis versicolor (also known as tinea versicolor). Each type has distinct characteristics and causes but shares the common feature of affecting the skin’s appearance. Pityriasis conditions are generally benign but can cause discomfort and cosmetic concerns. Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to treating these conditions, aiming to address the underlying causes and promote natural healing.
Symptoms
The symptoms of pityriasis vary depending on the specific type:
Pityriasis Rosea
- Herald Patch: A single, large, pink, scaly patch that appears first.
- Secondary Rash: Smaller, oval patches that follow, often in a Christmas-tree pattern on the back.
- Itching: The rash may be itchy, particularly in warm environments.
Pityriasis Alba
- Pale Patches: Light-colored, slightly scaly patches, typically on the face, neck, and upper limbs.
- Mild Itching: Occasionally, the patches may itch or cause mild discomfort.
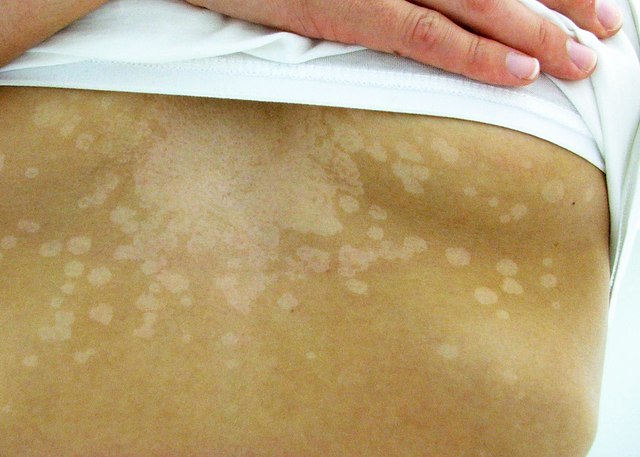
Pityriasis Versicolor
- Discolored Patches: White, pink, tan, or brown patches, usually on the trunk and shoulders.
- Scaling: Fine scaling may be present on the affected areas.
- Mild Itching: Sometimes, the patches can be mildly itchy.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing pityriasis:
- Age: Commonly affects children, adolescents, and young adults.
- Climate: Warm and humid climates can promote the growth of Malassezia yeast.
- Skin Type: Oily skin may be more susceptible to fungal infections.
- Immune Status: A weakened immune system can increase the risk.
- Genetics: Family history may play a role in the susceptibility to certain types of pityriasis.
Complications
While pityriasis is generally benign, complications can arise:
- Secondary Infections: Scratching can lead to bacterial infections.
- Cosmetic Concerns: Discolored patches can cause self-esteem issues, especially in visible areas.
- Chronicity: Some forms, like pityriasis versicolor, can recur frequently.
Preventions
Preventing pityriasis involves managing risk factors and maintaining good skin care practices:
- Hygiene: Regular bathing and skin care to reduce fungal overgrowth.
- Avoidance of Irritants: Using gentle skin care products to prevent irritation.
- Sun Protection: Using sunscreen to prevent discoloration and protect skin health.
- Moisturization: Keeping the skin hydrated to reduce dryness and scaling.
When to see a doctor
You should consult a healthcare provider if:
- The rash is widespread or persistent, lasting several weeks without improvement.
- Severe Itching: The itching is severe and affects daily activities.
- Signs of Infection: There are signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or pus.
- Uncertain Diagnosis: You are unsure of the diagnosis and need professional evaluation.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers individualized treatment plans to address the root causes and promote healing. A qualified homeopathic practitioner will conduct a detailed assessment to select the most appropriate remedy based on the individual’s overall health and specific symptoms.
Causes
The causes of pityriasis vary by type:
Pityriasis Rosea
- Unknown Origin: The exact cause is unknown, but it may be linked to viral infections.
Pityriasis Alba
- Hypopigmentation: Caused by a decrease in skin pigmentation, often related to eczema.
Pityriasis Versicolor
- Fungal Infection: Caused by the yeast Malassezia, which is part of the normal skin flora but can overgrow and cause symptoms under certain conditions.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing pityriasis involves:
- Clinical Examination: Visual inspection of the characteristic rash by a healthcare provider.
- Wood’s Lamp Test: Using ultraviolet light to examine the skin, particularly for pityriasis versicolor.
- Skin Scraping: Collecting skin samples to examine under a microscope or culture for fungal elements.
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s medical history and any recent illnesses or skin conditions.
Treatment
Treatment options for pityriasis depend on the specific type and severity:
Pityriasis Rosea
- Observation: The condition often resolves on its own within 6-8 weeks.
- Antihistamines: To relieve itching.
- Topical Steroids: To reduce inflammation and itching.
Pityriasis Alba
- Moisturizers: Regular use to prevent dryness.
- Topical Steroids: Mild steroids to reduce inflammation.
Pityriasis Versicolor
- Antifungal Creams: To eliminate the fungal infection.
- Oral Antifungal Medications: For widespread or resistant cases.
- Medicated Shampoos: Containing selenium sulfide or ketoconazole.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can support skin health and manage pityriasis:
- Regular Hygiene: Gentle cleansing to remove oils and prevent fungal growth.
- Cool Baths: To relieve itching and soothe irritated skin.
- Avoid Overheating: Staying cool and avoiding excessive sweating.
- Natural Remedies: Some natural remedies, such as aloe vera or coconut oil, may help soothe the skin, but consult a healthcare provider before use.
- Balanced Diet: A diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants to support immune health.
Preparing for your appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of the rash’s development, including any changes in size, color, and symptoms.
- Medical History: Provide information about any previous skin conditions, treatments, and recent illnesses.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes to manage pityriasis.
- Current Medications: List any current medications or supplements you are taking, including any topical treatments.

I won’t white stone skin,, medicine
Please help me sir..
I want white skin tone medicine
…