Mumps - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
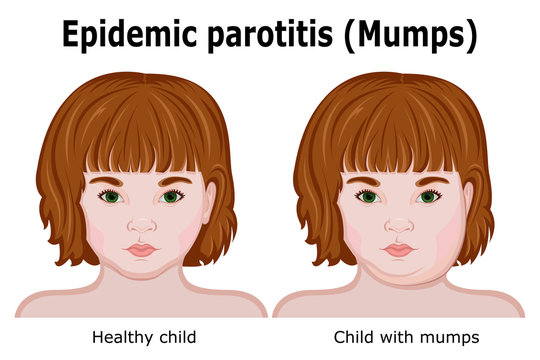
Mumps is a contagious viral infection characterized by swelling of the salivary glands, particularly the parotid glands located near the ears. It is caused by the mumps virus, which is part of the paramyxovirus family. Mumps was once common among children, but widespread vaccination has significantly reduced its prevalence. Despite this, outbreaks can still occur, and understanding the condition is essential for effective management and prevention.
Symptoms
Mumps symptoms typically appear 2 to 3 weeks after exposure to the virus and can include:
- Swelling of Salivary Glands: Swelling of one or both parotid glands, which can cause visible swelling in the cheeks and jaw.
- Fever: Elevated body temperature, often accompanied by chills and sweating.
- Headache: Persistent or severe headaches that may be associated with the swelling.
- Muscle Aches: Generalized body aches or muscle pain.
- Fatigue: General feeling of tiredness or weakness.
- Loss of Appetite: Reduced desire to eat, often due to discomfort or swelling in the mouth.
- Sore Throat: Discomfort or pain in the throat, which may accompany the swelling.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if:
- Persistent Symptoms: The symptoms are severe, worsening, or not improving with home care.
- High Fever: The child develops a high fever or exhibits signs of dehydration.
- Severe Swelling: The swelling of the salivary glands becomes severe or causes significant discomfort.
- Complications: There are signs of complications such as testicular pain or swelling (in males), severe headache, or neck stiffness.
- Uncertain Diagnosis: If you’re unsure whether the symptoms are due to mumps or another illness, consult a healthcare provider.
Causes
Mumps is caused by the mumps virus, which spreads through:
- Direct Contact: Contact with saliva or mucus from an infected person, such as through coughing, sneezing, or talking.
- Contaminated Surfaces: Touching surfaces contaminated with the virus and then touching the mouth or face.
- Shared Utensils: Using utensils or drinking from cups used by an infected person.
The virus is highly contagious and can spread easily in close-knit environments, such as schools or daycare centers.
Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of contracting mumps include:
- Unvaccinated Status: Lack of vaccination or incomplete vaccination against mumps.
- Close Contact: Being in close contact with an infected person, especially in crowded or enclosed spaces.
- Age: Mumps commonly affects children, though unvaccinated adults can also be at risk.
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems may be more susceptible to infections.
Complications
Complications of mumps can include:
- Orchitis: Inflammation of the testicles in males, which can cause pain, swelling, and potential fertility issues.
- Oophoritis: Inflammation of the ovaries in females, which may lead to abdominal pain and discomfort.
- Meningitis: Inflammation of the lining of the brain and spinal cord, which can cause severe headache, neck stiffness, and sensitivity to light.
- Hearing Loss: Temporary or permanent hearing loss can occur in rare cases.
- Encephalitis: Rarely, mumps can lead to inflammation of the brain, resulting in severe neurological symptoms.
Preventions
Preventing mumps involves:
- Vaccination: The MMR (measles, mumps, and rubella) vaccine is highly effective in preventing mumps. It is typically administered in two doses, starting at 12-15 months of age and a booster dose at 4-6 years.
- Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as regular hand washing and avoiding close contact with infected individuals.
- Avoiding Shared Items: Avoiding sharing utensils, cups, or other personal items that could be contaminated with the virus.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers supportive care for managing symptoms of mumps and promoting overall well-being. Some homeopathic remedies that may be considered include:
- Belladonna: For acute swelling and redness of the glands, with sudden onset of symptoms.
- Rhus Toxicodendron: For general soreness and muscle pain associated with mumps.
- Mercurius: For painful, swollen glands with a tendency to excessive salivation or bad breath.
- Lachesis: For cases with intense swelling and a tendency for the rash or swelling to shift locations.
A homeopathic practitioner can provide individualized remedies based on the child’s specific symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing mumps generally involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing the child’s medical history, vaccination status, and recent exposure to mumps or other contagious diseases.
- Physical Examination: Examining the child to assess symptoms such as swelling of the salivary glands and general health.
- Laboratory Tests: Conducting blood tests to detect antibodies or viral RNA specific to the mumps virus.
- Imaging: In some cases, imaging studies may be used to assess complications or severe symptoms.
Treatments
Treatment for mumps focuses on relieving symptoms and supporting recovery:
- Rest: Ensuring the child gets plenty of rest to help the body fight the infection.
- Hydration: Encouraging adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration and soothe throat discomfort.
- Pain Relief: Using over-the-counter pain relievers, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, to manage pain and fever.
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the swollen glands to alleviate discomfort.
- Isolation: Keeping the child away from others, especially in public places, to prevent the spread of the virus.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Supporting recovery at home can include:
- Comfort Measures: Offering soft, non-irritating foods and cool liquids to avoid further discomfort in the mouth and throat.
- Good Hygiene: Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent hand washing and cleaning surfaces that may be contaminated.
- Monitoring Symptoms: Keeping track of symptoms and any changes in the child’s condition to ensure appropriate care and follow-up.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of the child’s symptoms, including onset, severity, and any associated changes.
- List Vaccination Status: Bring information about the child’s vaccination history and any recent exposure to mumps or other infectious diseases.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns about the diagnosis, treatment options, or management strategies.
- Share Relevant History: Provide detailed information about the child’s medical history, including any known allergies or underlying health conditions.
