Metabolic Syndrome - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
What is Metabolic Syndrome?
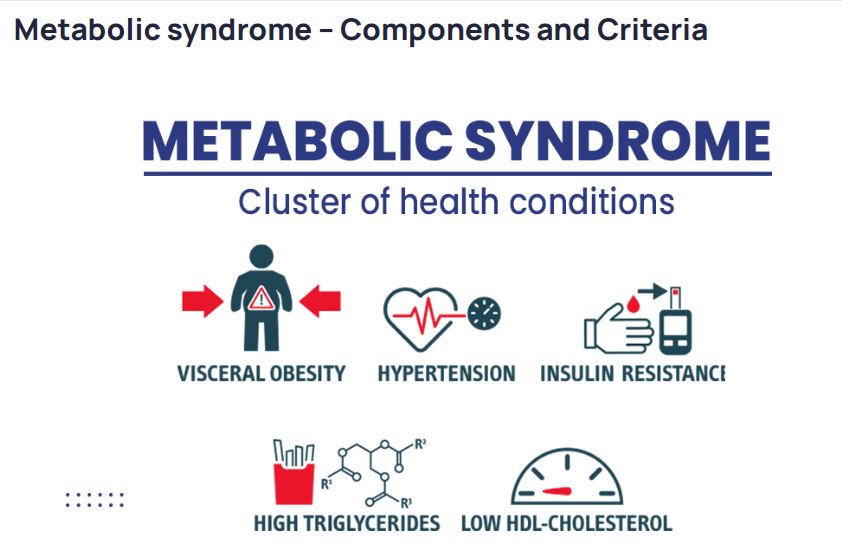
Metabolic Syndrome is not a single disease but a cluster of conditions that often occur together, increasing your risk of serious health problems. These conditions include:
Abdominal Obesity: This refers to excess fat around your waistline, also known as “belly fat.”
High Blood Pressure: Your blood pressure is consistently higher than the healthy range, putting strain on your heart and blood vessels.
High Blood Sugar: Elevated blood sugar levels that could be a precursor to diabetes or indicate insulin resistance.
Abnormal Cholesterol Levels: An imbalance in your cholesterol, with low levels of “good” HDL cholesterol and high levels of “bad” LDL cholesterol and triglycerides.
Why is it important to know about Metabolic Syndrome?
Having Metabolic Syndrome increases your risk of developing serious health conditions, such as heart disease, stroke, and diabetes. It’s like a red flag warning us that we need to take action to protect our health.
What causes Metabolic Syndrome?
Several factors contribute to the development of Metabolic Syndrome, including:
Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can lead to weight gain and metabolic disturbances.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles can contribute to weight gain and insulin resistance.
Genetics: Some people are genetically more predisposed to developing Metabolic Syndrome.
Age and Hormonal Changes: As we age, our metabolism may slow down, and hormonal changes can impact our weight and insulin sensitivity.
How can you manage Metabolic Syndrome?
The good news is that you can take charge of your health and manage Metabolic Syndrome through lifestyle changes. Here’s what you can do:
Healthy Eating: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Minimize processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive salt.
Regular Exercise: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activity each week. Incorporate strength training exercises two days a week.
Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of a healthy diet and regular exercise.
Blood Pressure Control: Monitor your blood pressure regularly, take any prescribed medications, and follow your doctor’s advice to keep it in a healthy range.
Blood Sugar Regulation: If you have diabetes or prediabetes, work closely with your healthcare provider to manage your blood sugar levels effectively.
Cholesterol Management: Adopt heart-healthy habits to keep your cholesterol levels in check. This includes reducing saturated and trans fats in your diet.
Remember:
Metabolic Syndrome is a wake-up call to take charge of your health and make positive changes in your life. It’s never too late to start making healthier choices. By working together, we can create a personalized plan to manage Metabolic Syndrome and reduce your risk of complications.
If you have any questions or concerns, don’t hesitate to reach out. Your health and well-being are my top priorities.
Wishing you the best of health.
Overview
Metabolic Syndrome is a cluster of conditions that occur together, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and type 2 diabetes. It is characterized by a combination of factors including high blood pressure, high blood sugar levels, excess body fat around the waist, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Addressing metabolic syndrome involves understanding its symptoms, causes, risk factors, and exploring both conventional and homeopathic treatment options.
Symptoms
Metabolic Syndrome often does not present clear symptoms, but it is identified through a combination of risk factors. Key signs and symptoms may include:
- Abdominal Obesity: Excess fat around the abdomen, often measured as a waist circumference of 40 inches or more in men and 35 inches or more in women.
- Hypertension: Elevated blood pressure levels, typically 130/85 mmHg or higher.
- Insulin Resistance: High blood sugar levels or symptoms of type 2 diabetes, such as frequent urination and excessive thirst.
- Dyslipidemia: Abnormal levels of lipids in the blood, including high triglycerides (150 mg/dL or higher) and low HDL (good) cholesterol (less than 40 mg/dL in men and 50 mg/dL in women).
- Fatigue and Weakness: General feelings of tiredness or lack of energy.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you:
- Experience Symptoms: Notice signs of abdominal obesity, high blood pressure, or abnormal blood sugar levels.
- Have Risk Factors: Have a family history of diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or metabolic syndrome.
- Need Regular Monitoring: Require regular health assessments due to high blood pressure, elevated blood sugar, or cholesterol levels.
- Seek Preventive Care: Want to address risk factors and prevent the development of related health conditions.
Causes
Metabolic Syndrome is influenced by various factors, and its causes are often multifactorial:
- Insulin Resistance: Cells in the body become less responsive to insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of metabolic syndrome, diabetes, or cardiovascular diseases can increase susceptibility.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Lack of physical activity contributes to weight gain and insulin resistance.
- Poor Diet: High intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and saturated fats.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and certain endocrine disorders can contribute.
- Chronic Stress: Long-term stress can lead to unhealthy eating habits and weight gain.
Risk Factors
Several risk factors increase the likelihood of developing metabolic syndrome:
- Obesity: Excess body fat, particularly around the abdomen.
- Age: Risk increases with age, especially over 40.
- Family History: A family history of diabetes, heart disease, or metabolic syndrome.
- Ethnicity: Higher prevalence in certain ethnic groups, such as Hispanic, African American, and Asian populations.
- Lifestyle Factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Hormonal Disorders: Conditions such as PCOS or hypothyroidism.
Complications
If left untreated, metabolic syndrome can lead to several serious health complications:
- Cardiovascular Disease: Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and coronary artery disease.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Progression to type 2 diabetes due to insulin resistance.
- Kidney Damage: Potential for chronic kidney disease or kidney failure.
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Accumulation of fat in the liver not related to alcohol consumption.
- Sleep Apnea: Increased risk of obstructive sleep apnea, which can further complicate metabolic syndrome.
Preventions
Preventing metabolic syndrome involves making lifestyle changes and managing risk factors:
- Healthy Diet: Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Limit processed foods, sugary beverages, and excessive salt.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling.
- Weight Management: Achieve and maintain a healthy weight through a combination of diet and physical activity.
- Stress Reduction: Practice stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Monitor blood pressure, blood sugar levels, and cholesterol levels regularly.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing metabolic syndrome by addressing individual symptoms and overall health. Common remedies include:
- Lycopodium: For symptoms related to digestive issues, abdominal bloating, and metabolic imbalances.
- Nux Vomica: To address issues associated with an unhealthy lifestyle, such as overeating and stress.
- Antimonium Crudum: For individuals with obesity and metabolic disturbances, especially when accompanied by digestive complaints.
A homeopathic practitioner can provide personalized remedies and treatment plans tailored to the individual’s specific symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing metabolic syndrome typically involves:
- Medical History: Review of symptoms, lifestyle factors, and family history.
- Physical Examination: Measurement of waist circumference, blood pressure, and overall physical assessment.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check glucose levels, cholesterol levels, and triglycerides.
- Additional Assessments: Evaluation for related conditions such as insulin resistance and fatty liver disease.
Treatments
Treatment for metabolic syndrome usually involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and medical management:
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthier diet, increasing physical activity, and achieving weight loss.
- Medications: Depending on the specific components of metabolic syndrome, medications may include:
- Antihypertensives: To manage high blood pressure.
- Statins: To control high cholesterol levels.
- Metformin: To improve insulin sensitivity and manage blood sugar levels.
- Monitoring and Management: Regular follow-ups to assess progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Supporting the management of metabolic syndrome through lifestyle changes and home remedies can be beneficial:
- Healthy Eating: Incorporate fiber-rich foods, reduce saturated fats, and avoid sugary snacks.
- Regular Physical Activity: Include activities such as walking, swimming, or resistance training.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water and limit sugary and caffeinated beverages.
- Stress Management: Practice relaxation techniques to reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
- Sleep Hygiene: Ensure adequate and quality sleep to support metabolic health.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner, consider:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of any symptoms, including changes in weight, energy levels, and overall health.
- List Medications and Supplements: Provide information about any current medications, supplements, or treatments.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns regarding your diagnosis, treatment options, and overall management.
- Health History: Share a comprehensive overview of your health history, including previous conditions, risk factors, and family history of metabolic syndrome.
