Fungal Infection - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
Fungal infections are caused by various types of fungi, including yeasts, molds, and dermatophytes. These infections can affect different parts of the body, such as the skin, nails, and internal organs. Fungal infections range from mild to severe, and while many are treatable with conventional medicine, homeopathic approaches offer a holistic perspective on managing these conditions. Understanding the nature of fungal infections, their symptoms, and effective management strategies can help in providing comprehensive care to patients.
Symptoms
The symptoms of fungal infections depend on the type of fungus and the area affected. Common symptoms include:
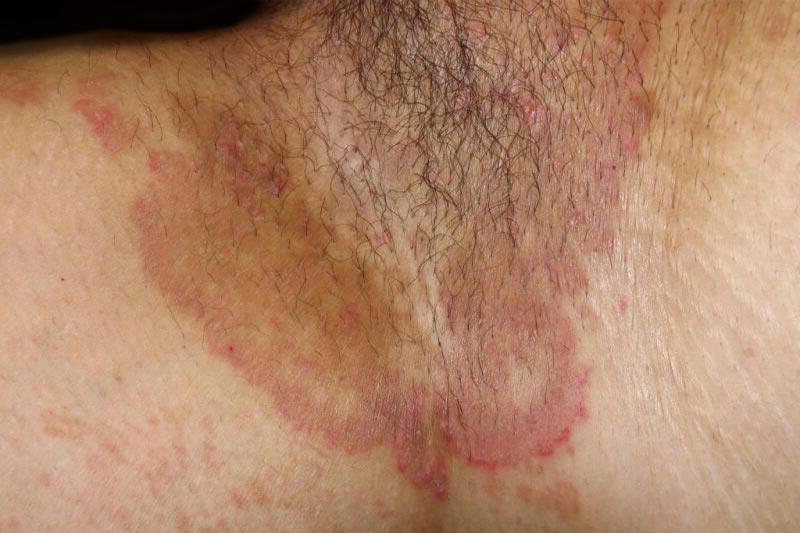
Skin Fungal Infections
- Itching: Persistent itching in the affected area.
- Redness: Inflamed, red patches or rashes.
- Scaling: Dry, flaky, or scaly skin.
- Blisters: Fluid-filled blisters or pustules.
Nail Fungal Infections
- Discoloration: Nails may turn yellow, brown, or white.
- Thickening: Nails may become thickened or deformed.
- Crumbly Texture: The nail surface may become brittle and break.
Internal Fungal Infections
- Fever: Elevated body temperature.
- Fatigue: Persistent tiredness and weakness.
- Cough: Persistent cough or difficulty breathing.
- Pain: Abdominal pain or discomfort.
When to see a doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms do not improve with over-the-counter treatments or home remedies.
- Severe Infection: The infection is spreading, causing significant discomfort, or affecting large areas of the body.
- Underlying Conditions: You have underlying health conditions that may increase the risk of complications.
- Systemic Symptoms: You experience systemic symptoms such as fever, chills, or severe fatigue.
Causes
Fungal infections are caused by fungi, which can be categorized into:
- Dermatophytes: Fungi that infect the skin, hair, and nails (e.g., ringworm, athlete’s foot).
- Yeasts: Fungi that commonly cause infections of the mucous membranes (e.g., Candida species causing oral thrush or vaginal yeast infections).
- Molds: Fungi that can cause infections in immunocompromised individuals (e.g., Aspergillus species).
Fungi thrive in warm, moist environments and can invade the body through direct contact or inhalation of spores.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing fungal infections:
- Weakened Immune System: Conditions such as diabetes, HIV/AIDS, or cancer can compromise the immune system.
- Antibiotic Use: Prolonged use of antibiotics can disrupt the natural balance of microorganisms and promote fungal overgrowth.
- Moist Environments: Frequent exposure to damp environments, such as swimming pools or communal showers.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene practices can increase the risk of fungal infections.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions such as eczema or psoriasis can create favorable conditions for fungal growth.
Complications
If left untreated, fungal infections can lead to complications:
- Secondary Bacterial Infections: Scratching or damaging the skin can lead to bacterial infections.
- Dissemination: Fungal infections can spread to other parts of the body, particularly in immunocompromised individuals.
- Chronic Infections: Persistent infections can cause long-term skin damage or nail deformities.
- Systemic Infections: Severe cases can lead to systemic fungal infections, affecting internal organs.
Preventions
To prevent fungal infections:
- Maintain Hygiene: Practice good personal hygiene, including regular washing and drying of skin and nails.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, shoes, or other personal items that come into contact with the skin.
- Keep Skin Dry: Wear breathable clothing and keep skin dry, especially in areas prone to moisture.
- Use Antifungal Products: Use antifungal powders or sprays in communal areas such as gyms or swimming pools.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly inspect skin and nails for any signs of infection, especially if at high risk.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a personalized approach to managing fungal infections by addressing the individual’s overall health and specific symptoms. Common homeopathic remedies for fungal infections include:
- Thuja Occidentalis: Useful for warts or skin infections with a tendency to recur.
- Sulphur: For itching, burning sensations, and skin irritation, especially when aggravated by warmth.
- Natrum Mur: For dry, scaly skin conditions, particularly if accompanied by a tendency to crack and bleed.
- Arsenicum Album: For infections with severe itching and burning, especially if relieved by warmth.
- Candida Albicans: Specifically targeted for yeast infections with symptoms like itching and discharge.
A homeopathic practitioner will assess the individual’s complete health picture, including physical, emotional, and psychological aspects, to select appropriate remedies.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing a fungal infection typically involves:
- Clinical Examination: Visual inspection of the affected area to assess characteristic signs of fungal infection.
- Microscopic Examination: A skin scraping or nail clipping is examined under a microscope to identify fungal elements.
- Culture Testing: A sample of the affected skin, nail, or mucous membrane is cultured to identify the specific fungus.
- Blood Tests: In cases of systemic infection, blood tests may be used to assess the extent of the infection and the body’s response.
Treatment
Treatment for fungal infections depends on the type and severity of the infection:
- Topical Antifungals: Creams, ointments, or sprays applied directly to the affected area (e.g., clotrimazole, terbinafine).
- Oral Antifungals: Pills or capsules for more severe or widespread infections (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole).
- Antifungal Shampoos: Special shampoos for scalp fungal infections (e.g., ketoconazole).
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Maintaining good hygiene and avoiding known triggers.
Lifestyle and home remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can complement conventional treatments:
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Applying diluted apple cider vinegar to the affected area may help balance pH and reduce fungal growth.
- Tea Tree Oil: Known for its antifungal properties, applying diluted tea tree oil can help manage skin fungal infections.
- Coconut Oil: Coconut oil has antifungal properties and can be used to moisturize and soothe affected areas.
- Garlic: Garlic contains natural antifungal compounds and can be applied topically or included in the diet.
- Probiotics: Consuming probiotics can help maintain a healthy balance of microorganisms and support overall immune function.
Preparing for your appointment
To ensure a productive appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of symptoms, including onset, duration, and any changes.
- Medical History: Provide information on any previous treatments, underlying health conditions, or known allergies.
- Lifestyle Factors: Share details about your daily habits, including exposure to potential fungal triggers or irritants.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and preventive measures.
