Warts - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
Warts are benign growths that appear on the skin due to the human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. They are common and can occur on various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, and genitals. Although warts are generally harmless, they can cause discomfort and affect self-esteem. While conventional treatments are widely used to manage warts, homeopathy offers a holistic approach that aims to treat the individual as a whole, addressing both physical and emotional aspects.
Symptoms
Warts are characterized by several distinct features:
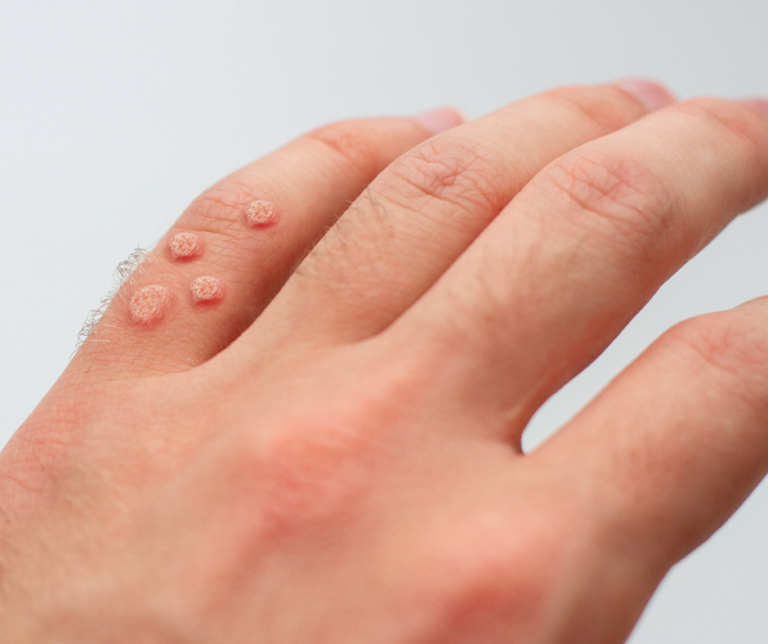
Common Warts
- Appearance: Small, rough, and raised growths, often with a cauliflower-like texture.
- Location: Typically found on the hands, fingers, or knees.
Plantar Warts
- Appearance: Hard, flat, and often calloused growths on the soles of the feet.
- Symptoms: Can cause pain or discomfort when walking or standing.
Flat Warts
- Appearance: Smooth, flat, and slightly raised, with a more even surface.
- Location: Usually found on the face, neck, or legs.
Genital Warts
- Appearance: Small, fleshy growths that may cluster or form larger lesions.
- Location: Found in the genital or anal area.
When to see a doctor
Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- Persistent Warts: Warts that do not respond to over-the-counter treatments or recur frequently.
- Pain or Discomfort: Warts causing significant pain or affecting daily activities.
- Rapid Growth: Warts that change in size, shape, or color.
- Bleeding or Discharge: Any bleeding, discharge, or other unusual changes in the wart.
Causes
Warts are caused by infection with certain types of HPV. The virus triggers an overgrowth of skin cells, leading to the formation of warts. HPV is highly contagious and can spread through:
- Direct Contact: Touching an infected person or contaminated surfaces.
- Broken Skin: Entering the body through small cuts or abrasions.
- Shared Objects: Using items such as towels or shoes that have come into contact with the virus.
Risk factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing warts:
- Weakened Immune System: Individuals with compromised immune systems are more susceptible.
- Frequent Hand Washing: Regular exposure to water and soap can damage the skin barrier, increasing risk.
- Shared Facilities: Using communal showers, pools, or locker rooms where the virus may be present.
- Personal Habits: Biting nails or picking at the skin can introduce the virus into the body.
Complications
While warts are usually benign, they can lead to complications:
- Spread of Infection: Warts can spread to other parts of the body or to other individuals.
- Secondary Infections: Scratching or picking at warts can lead to bacterial infections.
- Emotional Impact: Warts, particularly on visible areas, can affect self-esteem and cause psychological distress.
Preventions
To reduce the risk of developing warts or prevent their spread:
- Avoid Direct Contact: Refrain from touching warts or sharing personal items.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Wash hands regularly and keep the skin clean and dry.
- Protect Your Feet: Wear shoes in communal areas such as pools or locker rooms.
- Strengthen the Immune System: Maintain a healthy diet and lifestyle to support immune function.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a complementary approach to managing warts by treating the individual’s overall state of health and addressing the underlying imbalances. Homeopathic remedies are selected based on the patient’s specific symptoms and constitution. Some commonly used remedies include:
- Thuja Occidentalis: Often prescribed for warts that are rough, large, and have a cauliflower-like appearance. Useful for warts that bleed easily.
- Causticum: Recommended for warts that are painful and tend to bleed or have a tendency to become cancerous.
- Antimonium Crudum: Useful for warts with a hard, crusty surface, especially when located on the hands or feet.
- Sulphur: For warts with intense itching or burning sensations, often accompanied by a general feeling of unwellness.
- Nitricum Acidum: Applied for warts that are large, irregular, and tend to be painful.
A homeopathic practitioner will tailor the remedy to the individual’s specific symptoms and overall health condition.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing warts typically involves:
- Clinical Examination: A healthcare provider will visually inspect the growths and assess their characteristics.
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s medical history, including any recent exposure or symptoms.
- Biopsy: In some cases, a small sample of the wart may be taken and examined to rule out other conditions, such as skin cancer.
Treatment
Treatment options for warts vary and may include:
- Over-the-Counter Remedies: Products containing salicylic acid or other compounds that help to remove warts.
- Cryotherapy: Freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen to destroy the abnormal cells.
- Electrosurgery: Using electrical currents to burn off the wart.
- Laser Therapy: Applying a laser to remove the wart tissue.
- Prescription Medications: Stronger topical treatments or oral medications prescribed by a healthcare provider.
Lifestyle and home remedies
In addition to conventional treatments, several lifestyle and home remedies can support wart management:
- Soaking and Exfoliation: Soaking warts in warm water and gently exfoliating can help remove dead skin.
- Apple Cider Vinegar: Applying diluted apple cider vinegar to the wart may help dissolve the tissue.
- Garlic: Applying crushed garlic to the wart may have antiviral properties that can aid in its removal.
- Aloe Vera: Using aloe vera gel to soothe and promote healing of the affected area.
- Vitamin C: Applying crushed vitamin C tablets to the wart may help in treatment.
Preparing for your appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of the wart’s characteristics, including its size, location, and any associated symptoms.
- Medical History: Provide information about previous treatments or home remedies used.
- Treatment Goals: Be clear about your goals for treatment and any concerns you have.
- Questions: Prepare a list of questions about available treatment options, potential side effects, and management strategies.
- Support System: Consider bringing a family member or friend for additional support and perspective.
