Styes - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
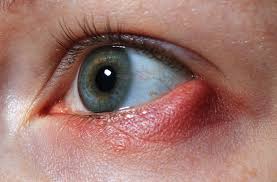
A stye, also known as a hordeolum, is a common, painful lump that forms on the eyelid. It is typically caused by a bacterial infection of the oil glands at the base of the eyelashes. Styes can occur on the inside or outside of the eyelid and often present as red, swollen, and tender areas. While most styes resolve on their own within a week, they can cause significant discomfort and may require treatment to alleviate symptoms.
Symptoms
The symptoms of a stye can vary in intensity and may include:
- Red, Swollen Lump: A small, red, and swollen bump on the eyelid, often near the edge.
- Pain and Tenderness: The affected area is usually painful and tender to the touch.
- Tearing: Increased tearing or watery eyes.
- Crusting: Crust forming around the eyelid.
- Itching: The eyelid may feel itchy.
- Blurred Vision: In some cases, blurred vision can occur if the stye presses against the eye.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if you experience:
- Persistent Stye: A stye that does not improve within a few days.
- Recurrent Styes: Frequent occurrences of styes.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision or difficulty seeing.
- Severe Pain: Intense pain that does not subside.
- Spread of Infection: Signs of the infection spreading, such as fever or redness extending beyond the eyelid.
Causes
Styes are caused by bacterial infections, most commonly due to Staphylococcus bacteria. Factors contributing to the development of styes include:
- Bacterial Infection: Infection of the oil glands in the eyelid.
- Poor Hygiene: Touching the eyes with unwashed hands or not cleaning contact lenses properly.
- Blocked Oil Glands: Blockage of the oil glands at the base of the eyelashes.
- Inflammation: Conditions such as blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelids).
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing styes:
- Poor Hygiene: Not washing hands regularly or touching the eyes frequently.
- Previous Styes: History of styes increases the likelihood of recurrence.
- Inflammatory Conditions: Conditions like blepharitis or rosacea.
- Use of Makeup: Using old or contaminated eye makeup.
- Contact Lenses: Not cleaning or handling contact lenses properly.
Complications
Although styes are generally not serious, complications can arise:
- Chalazion: A chronic, painless lump that forms if a stye does not fully heal.
- Spread of Infection: Rarely, the infection can spread to other parts of the eyelid or eye.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision or pressure on the eye if the stye is large.
Preventions
Preventing styes involves good hygiene and eye care practices:
- Hand Hygiene: Regularly wash hands with soap and water.
- Avoid Touching Eyes: Refrain from touching or rubbing the eyes.
- Clean Eyelids: Gently clean the eyelids with a mild soap or baby shampoo.
- Proper Makeup Use: Avoid sharing makeup, and regularly replace old or expired products.
- Contact Lens Care: Properly clean and handle contact lenses.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing styes, focusing on stimulating the body’s natural healing processes. Homeopathic remedies are selected based on individual symptoms and overall health.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Styes
- Staphysagria: For styes that recur frequently, especially after emotional stress.
- Pulsatilla: For styes that are painful and accompanied by thick, yellow discharge.
- Hepar Sulphuris: For styes that are painful, tender, and sensitive to touch.
- Silicea: For styes that are slow to heal and tend to recur.
- Apis Mellifica: For red, swollen, and stinging styes.
A qualified homeopathic practitioner will conduct a thorough assessment to select the most appropriate remedy based on the individual’s overall health, specific symptoms, and underlying causes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of a stye is usually straightforward and involves:
- Physical Examination: A doctor examines the eyelid and eye to assess the stye.
- Medical History: Reviewing the patient’s medical history and symptoms.
In most cases, no additional tests are needed unless there is a concern for other underlying conditions or complications.
Treatments
While most styes resolve on their own, treatments can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Conventional Treatments
- Warm Compresses: Apply warm compresses to the affected area for 10-15 minutes, several times a day, to reduce swelling and promote drainage.
- Avoid Squeezing: Do not squeeze or pop the stye, as this can spread the infection.
- Pain Relief: Use over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- Antibiotic Ointments: In some cases, antibiotic ointments or drops may be prescribed.
- Surgical Drainage: For persistent or large styes, minor surgical drainage may be necessary.
Homeopathic Treatments
Homeopathic treatments focus on individual symptoms and overall health. Commonly used remedies include:
- Staphysagria: For recurrent styes, particularly after emotional stress.
- Pulsatilla: For painful styes with thick, yellow discharge.
- Hepar Sulphuris: For tender and sensitive styes.
- Silicea: For slow-healing and recurrent styes.
- Apis Mellifica: For red, swollen, and stinging styes.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Certain lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage stye symptoms:
- Warm Compresses: Apply warm compresses to the affected area for 10-15 minutes, several times a day.
- Proper Hygiene: Maintain good hand and eye hygiene.
- Avoid Makeup: Refrain from using eye makeup until the stye has healed.
- Contact Lens Care: Properly clean and handle contact lenses.
- Avoid Squeezing: Do not attempt to squeeze or pop the stye.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of your symptoms, including their onset, duration, and any triggers.
- Medical History: Provide information about your personal and family medical history, including any history of eye conditions or styes.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes to manage styes.
- Current Medications: List any current medications or supplements you are taking, including any topical treatments.
