Uterine Polyp
- Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
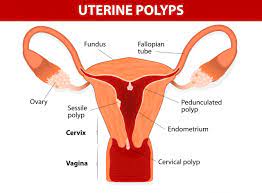
Uterine polyps are non-cancerous growths that develop on the inner lining of the uterus, known as the endometrium. These polyps can vary in size and number, and while they are often asymptomatic, they can cause a range of symptoms that affect reproductive health. Understanding uterine polyps is essential for managing symptoms effectively and exploring holistic treatment options, including homeopathy, can provide additional support.
What are Uterine Polyps?
Uterine polyps are growths that develop in the lining of the uterus (endometrium). These polyps are usually non-cancerous (benign) and vary in size, ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters. While uterine polyps can occur in women of any age, they are more common during the reproductive years.
Symptoms of Uterine Polyps
Some women with uterine polyps may experience no symptoms at all. However, others might notice the following signs:
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: This includes heavy or prolonged menstrual periods, irregular bleeding between periods, or postmenopausal bleeding.
Pelvic Pain: Some women may experience pelvic discomfort or pain, especially during menstruation.
Infertility: In some cases, uterine polyps may interfere with the implantation of a fertilized egg, leading to difficulties in conception.
Uterine polyps may not always present symptoms, but when they do, they can include:
- Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Irregular bleeding between periods, heavy menstrual bleeding, or bleeding after menopause.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Changes in the menstrual cycle, such as prolonged periods or spotting.
- Pelvic Pain: Discomfort or pain in the pelvic area, which can vary from mild to severe.
- Infertility: Difficulty conceiving or unexplained infertility may be associated with uterine polyps.
- Postmenopausal Bleeding: Any bleeding after menopause should be evaluated for potential uterine polyps.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Abnormal Bleeding: Unexplained or irregular bleeding that does not resolve with menstrual products.
- Persistent Pain: Ongoing pelvic pain or discomfort.
- Menstrual Irregularities: Significant changes in menstrual patterns or bleeding between periods.
- Difficulty Conceiving: Issues with fertility or difficulty becoming pregnant.
Causes
The exact cause of uterine polyps is not fully understood, but several factors may contribute:
- Hormonal Imbalances: Estrogen may play a role in the development of polyps as it stimulates the growth of the uterine lining.
- Genetic Factors: Genetic predisposition or family history of uterine conditions may increase the risk.
- Endometrial Changes: Abnormal changes in the endometrial lining can lead to the formation of polyps.
- Age: Polyps are more common in women between the ages of 40 and 50, but they can occur at any age.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase the risk of developing uterine polyps:
- Hormonal Therapy: Use of estrogen-based therapies or hormone replacement therapy.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese may contribute to hormonal imbalances that increase the risk of polyps.
- Family History: A family history of uterine polyps or other endometrial conditions.
- Age: Women in their 40s and 50s are at a higher risk, particularly those nearing menopause.
Complications
Uterine polyps can lead to several complications, including:
- Anemia: Heavy or prolonged bleeding from polyps can result in anemia, characterized by fatigue and weakness.
- Reproductive Issues: Polyps can affect fertility and may lead to complications during pregnancy.
- Persistent Symptoms: Ongoing bleeding or pain can impact quality of life and overall well-being.
- Cancer Risk: While uterine polyps are generally benign, there is a small risk of them containing cancerous cells, particularly in postmenopausal women.
Preventions
While uterine polyps cannot always be prevented, the following strategies may help reduce the risk or manage symptoms:
- Hormonal Management: Monitoring and managing hormonal levels through medical supervision or lifestyle changes.
- Healthy Lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and healthy weight to support overall health.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine gynecological exams to monitor reproductive health and detect any abnormalities early.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy, as a holistic approach to healing, aims to restore the body’s balance and promote natural healing mechanisms. In the case of uterine polyps, homeopathy can offer several potential benefits:
Symptomatic Relief: Homeopathic remedies are selected based on individual symptoms and their unique expression in each person. By addressing symptoms like abnormal bleeding and pelvic pain, homeopathy can provide relief and improve overall well-being.
Hormonal Balance: Homeopathy considers the hormonal imbalances that may contribute to the development of uterine polyps. Remedies chosen to restore hormonal equilibrium may help prevent the recurrence of polyps.
Non-Invasive Approach: Homeopathy is a non-invasive treatment method, and the remedies are prepared from natural substances, making them generally safe and devoid of adverse effects.
Improved Fertility: For women facing infertility due to uterine polyps, homeopathic treatment may help by reducing the size of polyps or promoting a healthier uterine environment for successful conception.
Homeopathy provides a holistic approach to managing uterine polyps by addressing individual symptoms and underlying imbalances. A homeopathic practitioner can provide personalized remedies and treatment plans tailored to individual symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing uterine polyps involves:
- Medical History: Reviewing symptoms, menstrual history, and overall health.
- Physical Examination: A pelvic exam to assess any physical abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: Ultrasound or hysterosonography (sonohysterography) to visualize the polyps and determine their size and location.
- Endometrial Biopsy: A procedure to obtain a tissue sample from the uterus for further examination and to rule out cancer.
Treatments
Treatment for uterine polyps may vary depending on the severity of symptoms and the presence of any related conditions:
- Medications: Hormonal treatments to manage symptoms or shrink polyps.
- Surgical Options: Hysteroscopic polypectomy, a minimally invasive procedure to remove polyps from the uterus.
- Observation: In cases where polyps are small and asymptomatic, a watch-and-wait approach may be recommended with regular monitoring.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes and home remedies can support symptom management:
- Healthy Diet: Include a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid excessive intake of processed foods and sugar.
- Regular Exercise: Engage in physical activity to support overall health and manage stress.
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to support general health and alleviate symptoms such as bloating.
- Herbal Remedies: Herbal teas like ginger or chamomile may help reduce inflammation and manage symptoms.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment with a healthcare provider or homeopathic practitioner, consider:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a detailed record of symptoms, including their onset, frequency, and impact on daily life.
- List Medications and Supplements: Bring information about any current medications or supplements you are taking.
- Prepare Questions: Write down any questions or concerns you have about your symptoms, treatment options, and overall health.
- Health History: Provide a comprehensive overview of your health history, including any existing conditions, family history of uterine polyps, and previous treatments.
