Blepharitis - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
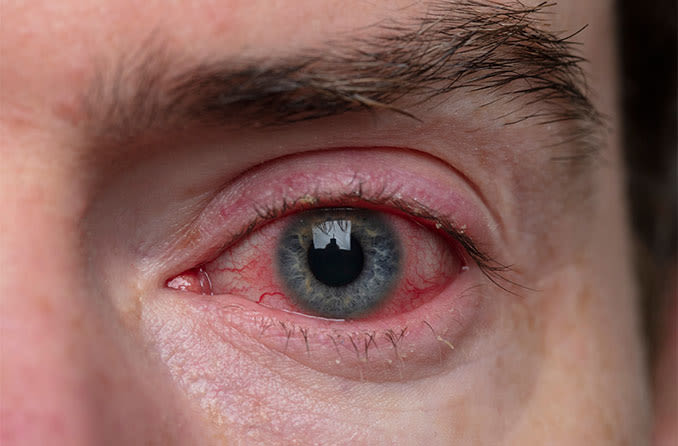
Blepharitis is a common and often chronic inflammation of the eyelid margins. It affects the area where the eyelashes grow and can lead to discomfort, itching, and redness. Blepharitis can be caused by various factors, including bacterial infections, seborrheic dermatitis, and meibomian gland dysfunction. Although it is not usually serious, it can be persistent and may significantly affect a person’s quality of life.
Symptoms
Blepharitis symptoms can vary but typically include:
- Red, Inflamed Eyelids: The eyelid margins may appear red and swollen.
- Itching and Burning: An itching or burning sensation in the eyes.
- Crusts or Scales: Formation of crusts or scales on the eyelid margins, especially upon waking.
- Watery or Dry Eyes: Increased tearing or dryness in the eyes.
- Gritty Sensation: Feeling of something foreign in the eye.
- Eye Discharge: Mucous or pus-like discharge from the eyes.
- Eyelash Problems: Eyelashes may become brittle or fall out.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you experience:
- Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms that do not improve with home care or over-the-counter treatments.
- Severe Discomfort: Intense itching, pain, or significant vision problems.
- Vision Changes: Any noticeable changes in vision or increased sensitivity to light.
- Repeated Episodes: Frequent recurrence of symptoms despite treatment.
- Signs of Infection: Increased redness, swelling, or discharge that suggests a possible infection.
Causes
Blepharitis can arise from multiple causes, including:
- Bacterial Infections: Particularly Staphylococcus bacteria, which can lead to inflammation and crusting.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: A common skin condition that can cause flaking and inflammation around the eyes.
- Meibomian Gland Dysfunction: Blockage or malfunction of the meibomian glands that produce the oily layer of tears.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to cosmetics, contact lenses, or environmental factors.
- Chronic Skin Conditions: Conditions such as psoriasis or eczema affecting the eyelid area.
Risk Factors
Factors that may increase the risk of developing blepharitis include:
- Previous Blepharitis: A history of blepharitis or other eyelid conditions.
- Skin Conditions: Existing skin conditions like seborrheic dermatitis or rosacea.
- Poor Eyelid Hygiene: Inadequate cleaning of the eyelid area.
- Contact Lens Use: Frequent or improper use of contact lenses.
- Allergies: Allergic reactions to cosmetics or environmental irritants.
- Chronic Conditions: Conditions that affect the skin or immune system.
Complications
While blepharitis itself is usually not serious, complications can include:
- Conjunctivitis: Infection of the conjunctiva (the clear membrane covering the white part of the eye).
- Chalazion: Blocked meibomian gland leading to a cyst.
- Stye (Hordeolum): A painful, swollen lump on the eyelid caused by an infection of an eyelash follicle.
- Vision Problems: Persistent blepharitis may lead to vision issues if left untreated.
- Scarring: Severe cases can lead to scarring of the eyelid margins.
Preventions
Preventing blepharitis involves maintaining good eyelid hygiene and managing risk factors:
- Regular Eyelid Hygiene: Clean your eyelids daily using warm water or eyelid wipes.
- Avoid Eye Irritants: Minimize exposure to allergens, harsh cosmetics, and irritants.
- Proper Contact Lens Care: Follow hygiene practices and recommendations for contact lens use.
- Manage Skin Conditions: Treat underlying skin conditions that may contribute to blepharitis.
- Healthy Diet: Maintain a diet that supports overall skin and immune health.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing blepharitis by addressing individual symptoms and overall health. Remedies are selected based on the specific characteristics of the patient’s condition. Common homeopathic remedies for blepharitis include:
Homeopathic Remedies for Blepharitis
- Calcarea Carbonica: For patients with chronic blepharitis, especially when associated with a sluggish or overweight constitution.
- Hepar Sulphuris: Useful for cases with intense inflammation, pain, and sensitivity to touch.
- Pulsatilla: For blepharitis with thick, yellow discharge and a tendency for symptoms to worsen in warm rooms.
- Sulphur: For chronic, itchy, and inflamed eyelids, particularly if worsened by heat and improved by cold.
- Staphysagria: For blepharitis with a history of trauma or emotional stress, and when there is a tendency for the condition to recur.
A homeopathic practitioner will select the appropriate remedy based on a detailed assessment of the patient’s symptoms and overall health.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing blepharitis typically involves:
- Medical History: Discussion of symptoms, previous occurrences, and any contributing factors.
- Physical Examination: Inspection of the eyelids and eyelashes for signs of inflammation, crusting, or discharge.
- Eyelid Examination: Assessing the condition of the meibomian glands and eyelid margins.
- Differential Diagnosis: Ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms, such as conjunctivitis or styes.
Treatments
Treatment for blepharitis often includes a combination of home care and medical interventions:
Conventional Treatments
- Warm Compresses: Applying warm compresses to the eyelids for 10-15 minutes, several times a day, to loosen crusts and improve gland function.
- Eyelid Hygiene: Daily cleaning with warm water or eyelid scrub pads to remove debris and reduce inflammation.
- Topical Antibiotics: Prescribed if a bacterial infection is suspected, often in the form of ointments or drops.
- Steroid Creams: Topical steroids may be used to reduce inflammation in more severe cases.
- Management of Underlying Conditions: Treating associated skin conditions or allergies contributing to blepharitis.
Homeopathic Treatments
Homeopathic remedies can complement conventional treatments and support overall health:
- Arsenicum Album: For dry, burning, and inflamed eyelids, often with a tendency towards anxiety.
- Graphites: For thickened, crusty eyelid margins with a tendency towards sticky discharge.
- Natrum Muriaticum: For blepharitis with dry, scaly patches on the eyelids and a tendency for symptoms to worsen in sunlight.
- Rhus Toxicodendron: For itching and burning in the eyelids, especially if improved by warmth.
- Silicea: For chronic blepharitis with a tendency to develop chalazions or other eyelid cysts.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage and prevent blepharitis:
- Regular Eyelid Cleaning: Gently clean your eyelids daily with warm water or eyelid wipes to maintain hygiene.
- Avoid Eye Makeup: Refrain from using eye makeup during flare-ups and ensure proper removal of makeup.
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants to support skin health.
- Manage Allergies: Identify and avoid allergens or irritants that may contribute to blepharitis.
- Hydrate: Drink plenty of water to keep your body and skin hydrated.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment, consider the following:
- Symptom Record: Keep a record of your symptoms, including their onset, duration, and any factors that worsen or improve them.
- Medical History: Provide detailed information about any previous episodes of blepharitis or related conditions.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and preventive measures.
- Current Medications: List any medications, supplements, or homeopathic remedies you are currently taking.
