Purpura Haemorrhagica - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
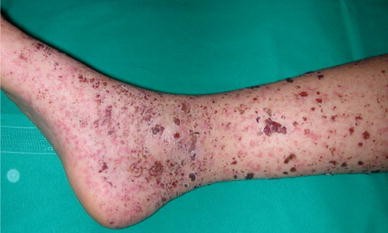
Purpura Haemorrhagica, also known as Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) when referring to the immune-mediated form, is a condition characterized by a low platelet count (thrombocytopenia) leading to bleeding and bruising under the skin. It is important to note that “purpura” refers to a type of bleeding disorder where purplish spots or patches appear on the skin due to small blood vessel leakage. Haemorrhagica denotes a more severe form of bleeding, and the term can sometimes be used to describe various conditions with bleeding tendencies.
Symptoms
The symptoms of Purpura Haemorrhagica can vary based on the severity of the condition and may include:
- Purpura: Large, purple or red spots and patches on the skin, particularly on the legs, arms, and buttocks.
- Petechiae: Small, pinpoint red or purple spots that appear on the skin.
- Bruising: Easy bruising with minimal or no trauma.
- Bleeding: Unexplained bleeding from the gums, nosebleeds, or in the urine or stool.
- Fatigue: General fatigue or weakness due to blood loss.
- Joint Pain: Some individuals may experience joint pain or swelling.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if you notice:
- Persistent Bleeding: Unexplained or persistent bleeding, including nosebleeds or bleeding gums.
- Severe Bruising: Large or unusual bruises that appear without obvious cause.
- Purpura: New or worsening purpura or petechiae.
- Fatigue: Unusual fatigue or weakness that accompanies bleeding symptoms.
- Medical History: If you have a history of bleeding disorders or other relevant health conditions.
Causes
Purpura Haemorrhagica can result from various underlying conditions or causes, including:
- Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP): An autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets.
- Viral Infections: Certain viral infections, such as hepatitis C or HIV, can cause thrombocytopenia.
- Medications: Some medications, like anticoagulants or certain antibiotics, can lead to decreased platelet counts.
- Bone Marrow Disorders: Conditions affecting bone marrow function, such as leukemia or aplastic anemia, can impact platelet production.
- Nutritional Deficiencies: Deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12 or folate, can contribute to thrombocytopenia.
- Chronic Diseases: Chronic diseases, including liver disease or kidney failure, may affect platelet counts.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for Purpura Haemorrhagica include:
- Age: It can affect individuals of any age, though ITP is often diagnosed in children and adults.
- Gender: Women are more frequently affected by ITP compared to men.
- Family History: A family history of bleeding disorders or autoimmune diseases may increase the risk.
- Autoimmune Diseases: Individuals with other autoimmune disorders are at higher risk.
- Medication Use: Long-term use of certain medications, especially those affecting blood clotting, can increase risk.
Complications
Potential complications of Purpura Haemorrhagica include:
- Severe Bleeding: Risk of serious bleeding complications, such as gastrointestinal bleeding or internal bleeding.
- Organ Damage: Repeated or severe bleeding episodes may lead to damage of organs or tissues.
- Anemia: Chronic bleeding can lead to anemia due to a decrease in red blood cells.
- Infection: In cases where bone marrow disorders are involved, there is an increased risk of infections.
Preventions
Preventing Purpura Haemorrhagica involves managing risk factors and maintaining overall health:
- Avoid Trauma: Minimize activities that can lead to bruising or bleeding.
- Medication Management: Use medications with caution and under medical supervision, especially anticoagulants.
- Healthy Diet: Ensure adequate intake of vitamins and minerals necessary for healthy blood and platelet function.
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular medical check-ups and monitoring if you have a history of bleeding disorders.
- Vaccination: Stay up-to-date with vaccinations to prevent infections that could impact platelet count.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing Purpura Haemorrhagica by addressing the individual’s overall health and specific symptoms. Remedies are chosen based on the individual’s unique presentation and overall health condition.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Purpura Haemorrhagica
- Arnica Montana: For bruising and trauma-related bleeding. It can help reduce pain and promote healing.
- Phosphorus: For bleeding tendencies with a tendency to hemorrhage easily. Helpful in cases with excessive bleeding from the gums or nose.
- Hamamelis: Useful for bleeding from veins, with a focus on improving circulation and reducing bleeding.
- Secale Cornutum: For cases with excessive bleeding and a feeling of weakness or faintness.
- Carbo Vegetabilis: For severe cases of bleeding with weakness and a need for improved circulation.
A qualified homeopathic practitioner will evaluate the individual’s symptoms and overall health to select the most appropriate remedy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of Purpura Haemorrhagica involves:
- Medical History: Detailed discussion of symptoms, family history, and any underlying conditions.
- Physical Examination: Examination of the skin to identify characteristic features of purpura and petechiae.
- Blood Tests: Complete blood count (CBC) to determine platelet levels and assess other blood components.
- Bone Marrow Biopsy: If a bone marrow disorder is suspected, a biopsy may be performed to evaluate marrow function.
- Coagulation Tests: Tests to assess blood clotting and rule out other bleeding disorders.
- Imaging Studies: In some cases, imaging studies may be needed to assess internal bleeding or organ damage.
Treatments
Treatment for Purpura Haemorrhagica typically involves addressing the underlying cause and managing symptoms:
Conventional Treatments
- Medications: Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation and immune response in cases of ITP. Other medications may include immune suppressants or medications to increase platelet production.
- Blood Transfusions: In severe cases, platelet transfusions may be necessary to manage bleeding.
- Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG): To boost platelet counts and reduce bleeding tendencies in some cases.
- Splenectomy: Surgical removal of the spleen may be considered in chronic cases where the spleen is destroying platelets.
Homeopathic Treatments
Homeopathic treatments are tailored to the individual and may include remedies such as:
- Arnica Montana: For bruising and trauma-related bleeding.
- Phosphorus: For general bleeding tendencies and weakness.
- Hamamelis: For bleeding from veins and circulatory issues.
- Secale Cornutum: For excessive bleeding and weakness.
- Carbo Vegetabilis: For severe bleeding with weakness and circulation issues.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage Purpura Haemorrhagica:
- Healthy Diet: Include foods rich in vitamins C and K, which support blood vessel health and platelet function.
- Avoid Blood Thinners: Avoid foods and substances that may increase bleeding risk, such as excessive alcohol and certain supplements.
- Manage Stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities to support overall health.
- Protect the Skin: Use protective measures to prevent bruising or injury.
- Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor symptoms and platelet levels as advised by your healthcare provider.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of symptoms, including their onset, duration, and any associated factors.
- Medical History: Provide detailed information about your medical history, including any previous bleeding disorders or underlying conditions.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes.
- Current Medications: List any medications or supplements you are currently taking.
