Seborrhoea - Symptoms, Causes, Prevention & Homeopathic treatment
Overview
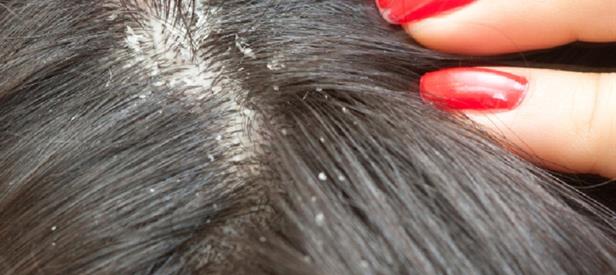
Seborrhoea, commonly known as seborrheic dermatitis, is a chronic skin condition characterized by an overproduction of sebum (oil) that leads to inflammation, redness, and flaking. This condition primarily affects areas of the skin rich in oil glands, such as the scalp, face, and upper trunk. Seborrhoea can range from mild dandruff to more severe forms with significant skin lesions.
Symptoms
The symptoms of seborrhoea can vary in severity and location but generally include:
- Flaky Scales: White or yellowish flakes on the scalp, face, or other affected areas.
- Redness: Inflamed, red patches of skin.
- Itching: Pruritus or itching is common and can be bothersome.
- Greasy Skin: Oily or greasy patches of skin, often accompanied by flakes.
- Crusting: In severe cases, the skin may develop crusts or plaques.
When to See a Doctor
Consult a healthcare provider if:
- Persistent Symptoms: Symptoms persist despite over-the-counter treatments or home remedies.
- Severe Discomfort: The condition causes significant itching, discomfort, or pain.
- Spread: Symptoms spread to other areas of the body or become severe.
- Signs of Infection: If you notice signs of infection, such as increased redness, warmth, or pus.
- Non-Responsive to Treatments: If conventional treatments or lifestyle changes are not effective.
Causes
The exact cause of seborrhoea is not fully understood, but several factors contribute to its development:
- Overactive Sebaceous Glands: Excess production of sebum by the oil glands.
- Malassezia Yeast: A type of fungus that naturally resides on the skin and may contribute to inflammation.
- Genetic Factors: A family history of seborrheic dermatitis or other skin conditions.
- Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations, particularly androgens, can influence sebum production.
- Stress: Emotional stress and fatigue may exacerbate symptoms.
Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing seborrhoea:
- Family History: A family history of seborrheic dermatitis or similar skin conditions.
- Age: More common in infants (cradle cap) and adults aged 30-60.
- Skin Type: Oily skin types are more prone to seborrhoeic dermatitis.
- Other Conditions: Individuals with conditions like Parkinson’s disease or HIV are at higher risk.
- Environmental Factors: Cold, dry climates and seasonal changes can exacerbate symptoms.
Complications
Complications from seborrhoea can include:
- Secondary Infections: Bacterial or fungal infections can develop in areas affected by seborrhoea.
- Scarring: Chronic inflammation may lead to scarring in severe cases.
- Psychological Impact: Persistent symptoms can affect self-esteem and quality of life.
Preventions
Preventing seborrhoea involves minimizing triggers and maintaining skin health:
- Regular Cleansing: Use mild, non-irritating shampoos and cleansers to manage oil production.
- Avoid Irritants: Avoid products that may exacerbate symptoms, such as harsh soaps or alcohol-based lotions.
- Stress Management: Practice stress-relief techniques, as stress can worsen symptoms.
- Balanced Diet: Eat a balanced diet to support overall skin health and reduce inflammation.
- Climate Control: Use a humidifier in dry climates to maintain skin moisture.
Can Homeopathy Help?
Homeopathy offers a holistic approach to managing seborrhoea by addressing individual symptoms and overall health. Remedies are chosen based on the patient’s specific presentation and underlying health conditions.
Common Homeopathic Remedies for Seborrhoea
- Sulphur: For dry, itchy skin with a tendency to become worse with warmth and better with cold applications.
- Graphites: Effective for thick, sticky scales and cracked skin, particularly on the scalp and behind the ears.
- Arsenicum Album: For itchy, burning skin with dryness and restlessness.
- Petroleum: For dry, rough skin with severe itching and irritation, especially in winter.
- Calcarea Carbonica: Useful for greasy, itchy skin with flaking, particularly in those who feel chilly.
A qualified homeopathic practitioner will evaluate individual symptoms and health history to select the most appropriate remedy.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing seborrhoea involves:
- Medical History: Discussion of personal and family medical history, including skin conditions and other health issues.
- Physical Examination: A thorough examination of the affected skin to identify characteristic features of seborrhoea.
- Skin Scraping: In some cases, skin scrapings may be examined under a microscope to rule out fungal infections.
- Patch Testing: If an allergic reaction is suspected, patch testing may be performed to identify potential allergens.
Treatments
Treatment for seborrhoea typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications, topical treatments, and sometimes systemic medications:
Conventional Treatments
- Topical Antifungals: Shampoos or creams containing ketoconazole or selenium sulfide can reduce Malassezia yeast levels.
- Topical Corticosteroids: Reduces inflammation and itching in more severe cases.
- Medicated Shampoos: Shampoos containing tar or zinc pyrithione can help manage symptoms.
- Emollients: Moisturizers and emollients to maintain skin hydration and barrier function.
Homeopathic Treatments
Homeopathic treatments are tailored to the individual and may include remedies such as:
- Sulphur: For symptoms worsening with warmth and better with cold.
- Graphites: For sticky, thick scales and cracked skin.
- Arsenicum Album: For burning, itchy skin with dryness.
- Petroleum: For severe itching and dry, rough skin.
- Calcarea Carbonica: For greasy skin with flaking.
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Incorporating lifestyle changes and home remedies can help manage seborrhoea:
- Maintain Good Hygiene: Regularly cleanse the affected areas with mild, non-irritating products.
- Use Moisturizers: Apply fragrance-free moisturizers to keep the skin hydrated.
- Avoid Hot Water: Use lukewarm water for washing to prevent skin dryness.
- Healthy Diet: Include omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants in your diet to support skin health.
- Manage Stress: Engage in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, or yoga.
Preparing for Your Appointment
To make the most of your appointment:
- Document Symptoms: Keep a record of symptoms, including their onset, duration, and any potential triggers.
- Medical History: Provide information about your personal and family medical history, including any other skin conditions or health issues.
- Questions: Prepare questions about treatment options, potential side effects, and lifestyle changes.
- Current Medications: List any current medications or supplements you are taking.
